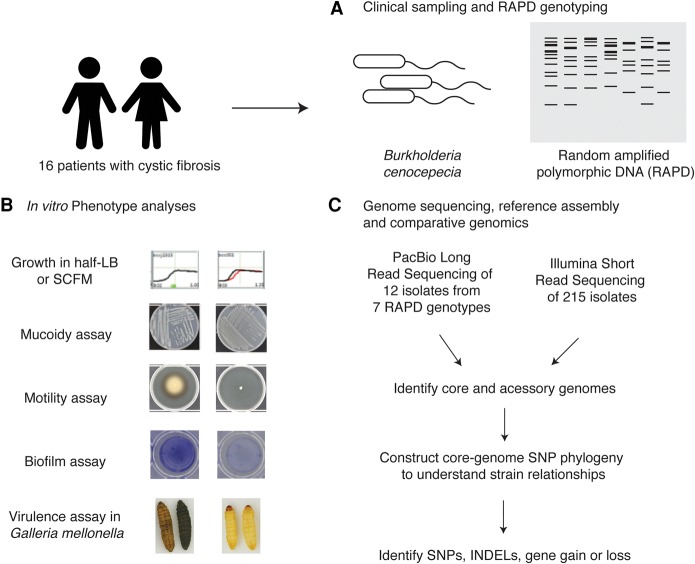
Figure 1.
Overview of data collection. (A) To understand the genomic and phenotypic evolution of B. cenocepacia strains within the CF lung, we examined 16 longitudinal series of B. cenocepacia strains isolated from sputum (215 isolates total) that had been collected and typed using RAPD analysis as part of the surveillance program at CBCCRRR. (B) In vitro phenotypic analyses were carried out for all isolates, focusing on clinically relevant traits: growth rate, motility, biofilm formation, mucoidy, and acute virulence in an insect model system. (C) Short-read paired-end sequencing by Illumina was carried out for all 215 isolates. To provide reference-quality sequences for a subset of isolates representing all seven RAPD genotypes, long-read sequencing by PacBio was carried out on 11 isolates as well as on the reference B. cenocepacia J2315 as a control.