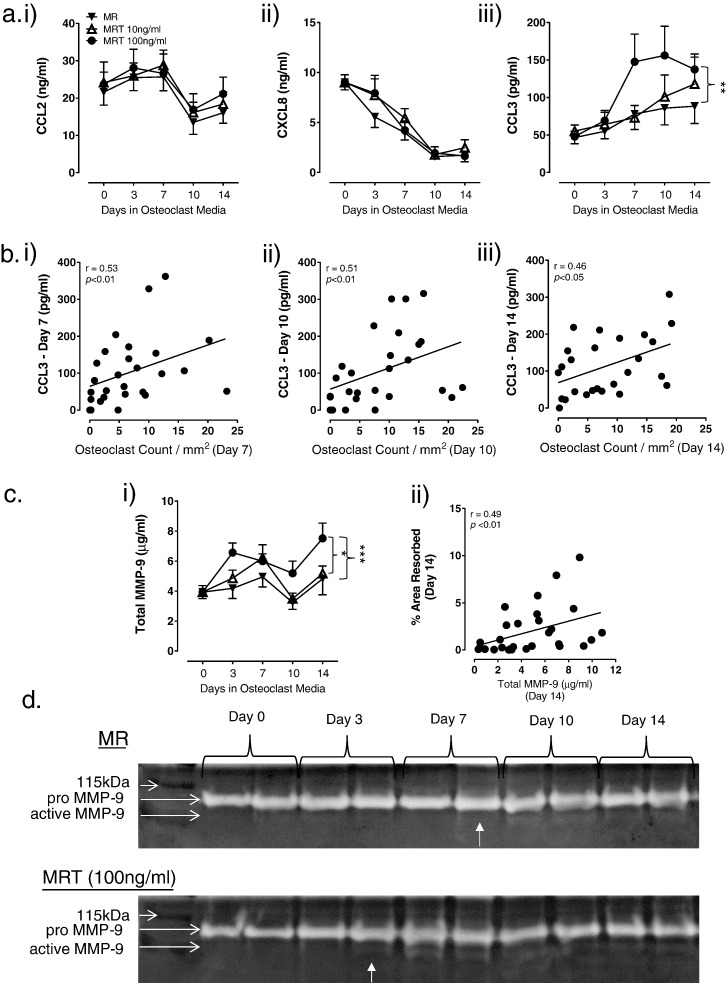
Fig. 5.
TL1A concentration-dependently increases expression of the osteoclastogenic chemokine CCL3 and gelatinase MMP-9.
CD14+ monocytes were isolated from pre-menopausal females (n = 7). Cells were cultured on ivory discs for 7 days in media + MCSF and further differentiated for 7, 10 or 14 days in the presence of MCSF (M) and RANKL (R) ± TL1A (T) at 10 ng/ml or 100 ng/ml. Culture supernatants were collected at indicated time-points and tested for a) i) CCL2, ii) CXCL8 and iii) CCL3. Significantly increased CCL3 levels were detected across the time-course in 100 ng/ml TL1A cultures compared to control (p < 0.01). No differences were observed in CCL2 and CXCL8 levels. b) CCL3 levels significantly correlated with OC numbers at (i) day 7, (ii) day 10 and (ii) day 14. c) i) Significantly increased total MMP-9 expression was observed in the 100 ng/ml TL1A cultures across the time-course compared to control (p < 0.0001) and 10 ng/ml TL1A cultures (p < 0.05). ii) Levels of total MMP-9 significantly correlated with % area resorbed at day 14. d) Levels of pro- and active-MMP-9 in cultures were determined by gelatine zymography (n = 4). Representative zymograms for control (MR) and 100 ng/ml TL1A (MRT) cultures. Pro-MMP-9 was detected in both cultures across the time-course. Active MMP-9 was first detected at day 3 in the 100 ng/ml TL1A OC cultures and day 7 in control cultures. Samples run in duplicate. Statistical analysis performed with 2-Way ANOVA and Spearman correlation.