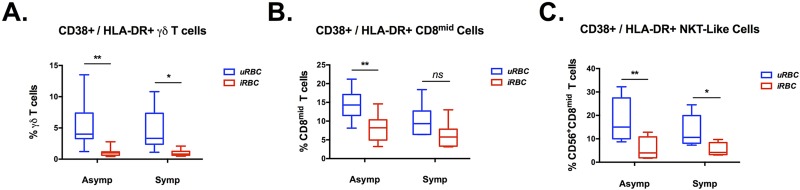
Fig 5. Analysis of CD38+/HLA-DR+ activation status of T cell sub-populations in asymptomatic and symptomatic malaria patients.
Co-expression of CD38 and HLA-DR on T cells has been suggested as a marker of activation for malaria reactive T cells. The expression of these surface markers was analyzed in T cell subpopulations from asymptomatic (n = 9) and symptomatic (n = 6) patient PBMCs during exposure to P. falciparum strain H1064 infected erythrocytes (iRBC lysate) or uninfected erythrocytes (uRBC). Exposure to P. falciparum antigens diminished the activation status of γδ T cells (A), CDmid T cells (B), and NKT-like T cells (C). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test (iRBC lysate vs. uRBC for each patient). * = p-value < 0.05, ** = p-value < 0.01.