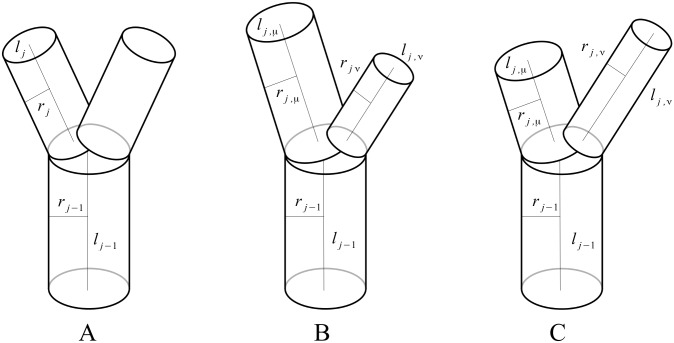
Fig 1. Diagram of symmetric and asymmetric bifurcations.
Symmetric branching (A) is characterized by every branch within a given generation j having equal values of radius and length. Positive asymmetry (B) is such that one child branch is larger than the other in both radius and length. Negative asymmetry (C) is such that one child branch has a larger radius and shorter length while the other has a smaller radius and greater length.