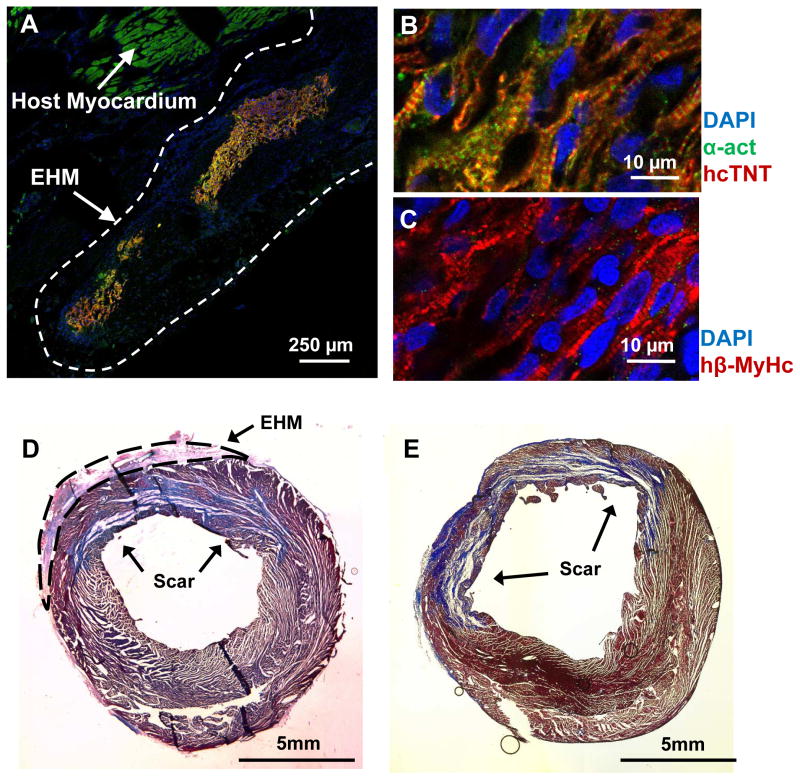
Figure 2. Immunofluorescence showed viable human cardiomyocytes 4 weeks after transplantation of engineered heart muscle.
(A) Transplanted engineered heart muscle (EHM) led to the engraftment of human cardiomyocytes on the host heart. Partially aligned sarcomeres could be detected in viable human cardiomyocytes when staining for (B) alpha actinin (α-act), human cardiac troponin T (hcTnT), and (C) human beta myosin heavy chain (hβ-MyHc). Despite substantial engraftment and survival of human cardiomyocytes, scar sizes between (D) EHM (n=4) and (E) control groups (n=4) were similar (p=0.48) as assessed by Masson’ trichrome staining (blue color).