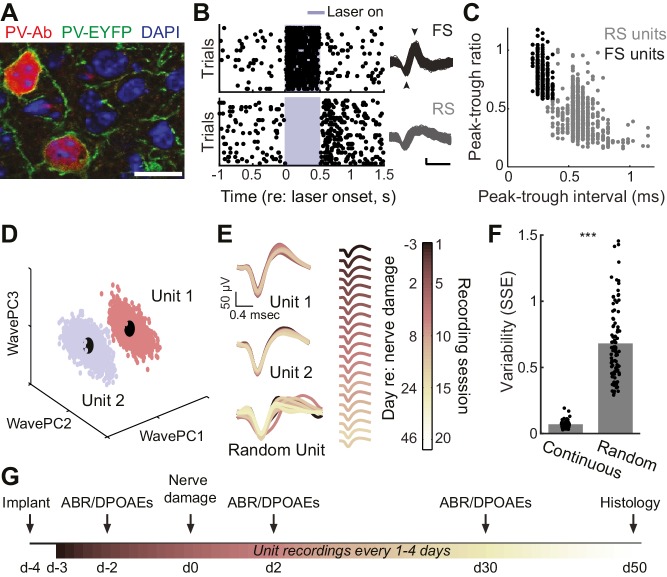
Figure 1. Approach for chronic single unit recordings and optogenetic activation in mouse A1.
(A) Immunolabeling of PV neurons in A1 with co-localization of EYFP reporter in Pv-Cre:Ai32 transgenic mice. DAPI labels cell nuclei. Scale bar = 15 µm. (B) Spike raster plots illustrating that optogenetic activation of fast spiking (FS) PV+ units (black, top) inhibits regular spiking (RS) units (gray, bottom). Right, spike waveforms for the RS and FS units. Arrowheads denote spike peak and trough. Scale bars, 0.5 ms and 50 µV. (C) Scatter plot showing the bimodal distribution of peak-tough amplitude and timing differences across all RS (gray) and FS (black) units. (D) A random sub-sampling of spike waveforms recorded over 53 days from a single wire of a tetrode projected down into the first three principal components (PC). (E) Spike waveforms from the two units identified in (D) across all recording sessions, color-coded and superimposed chronologically. Waveforms for random units were selected at random from all simultaneously recorded units. (F) The variability in the actual unit waveforms, estimated as the sum of squared errors (SSE), is significantly less than randomly shuffled units (p<0.001, f(1)=814.73, mean ± SEM). (G) Experimental design.
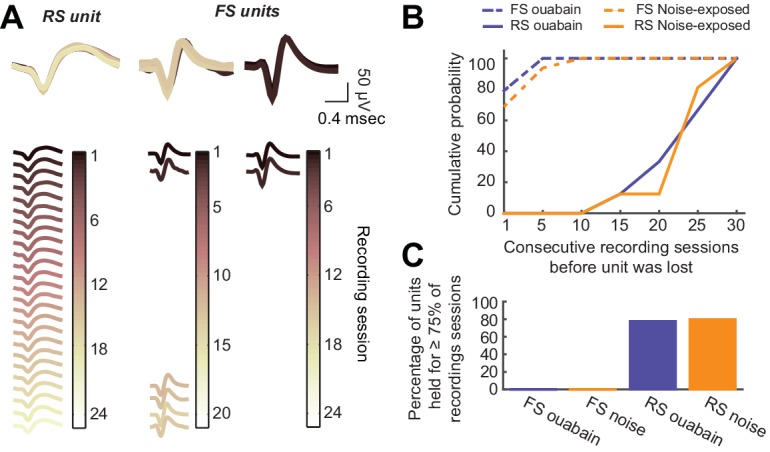
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Long-term tetrode recordings from isolated single units is feasible with RS neurons, but not FS neurons.