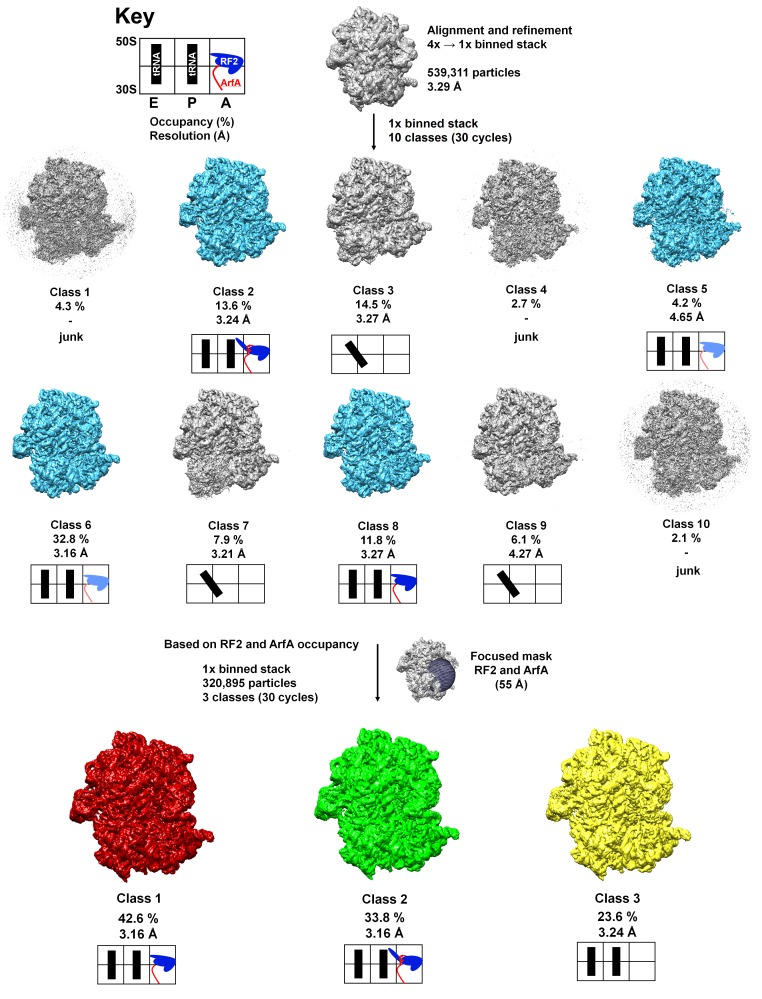
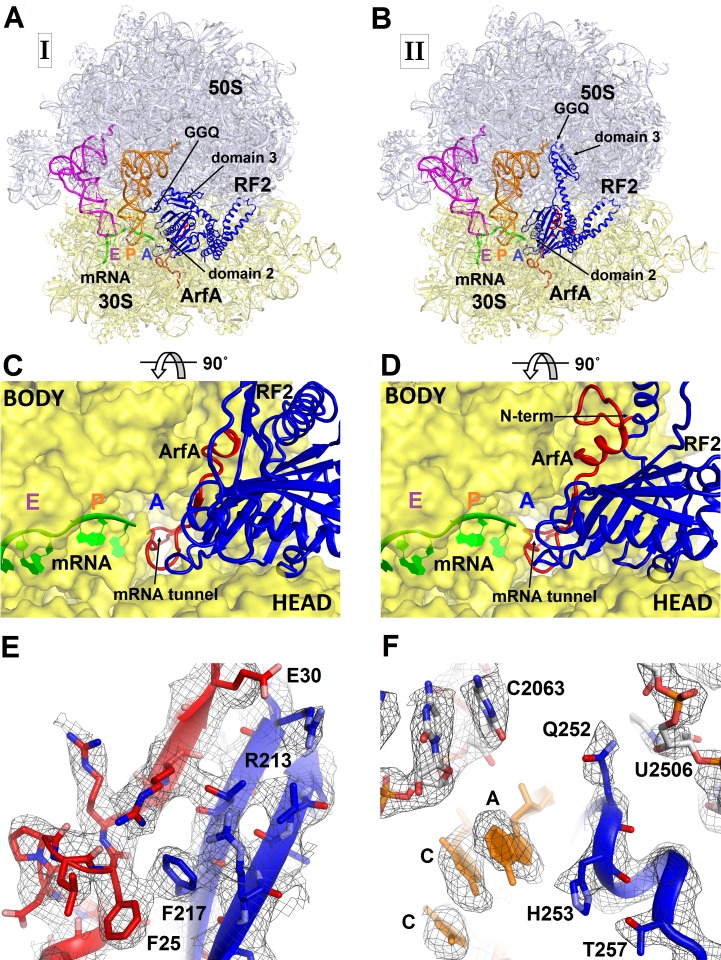
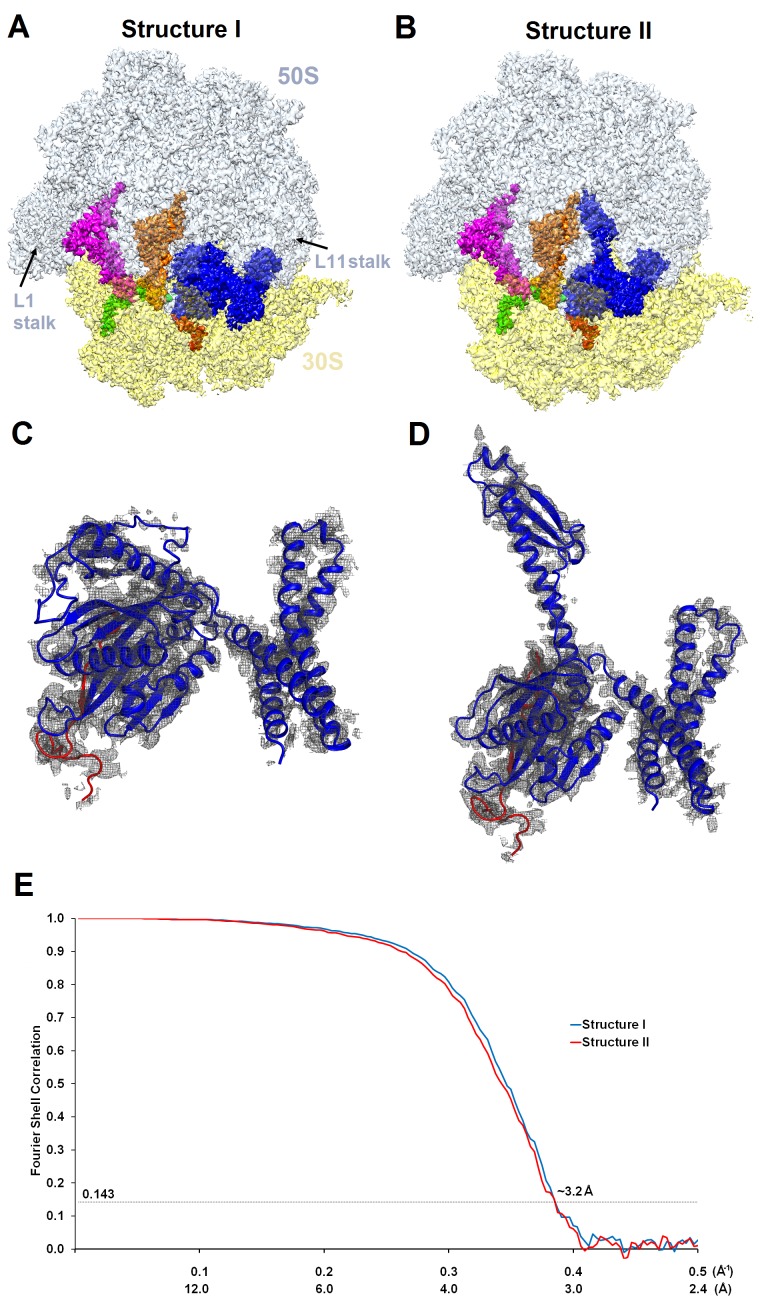
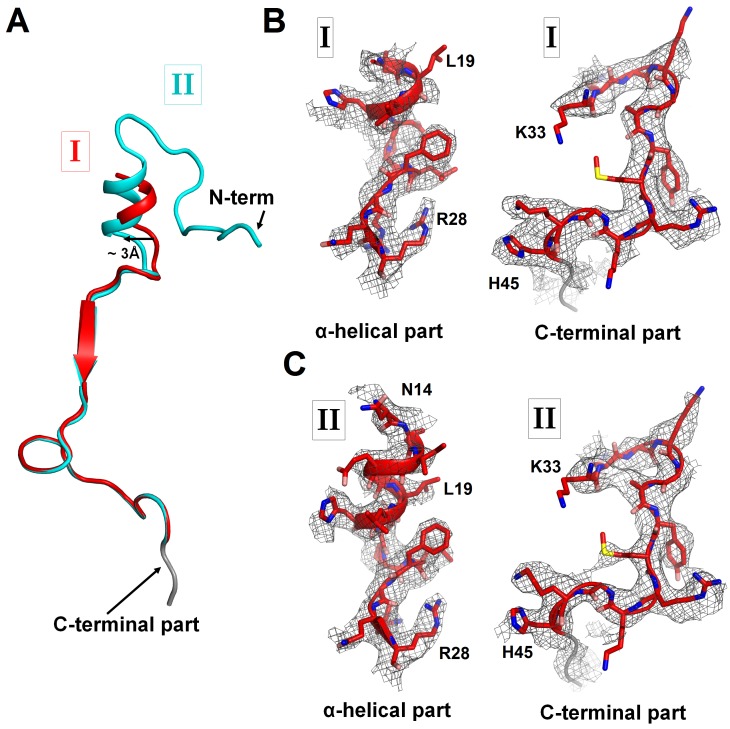
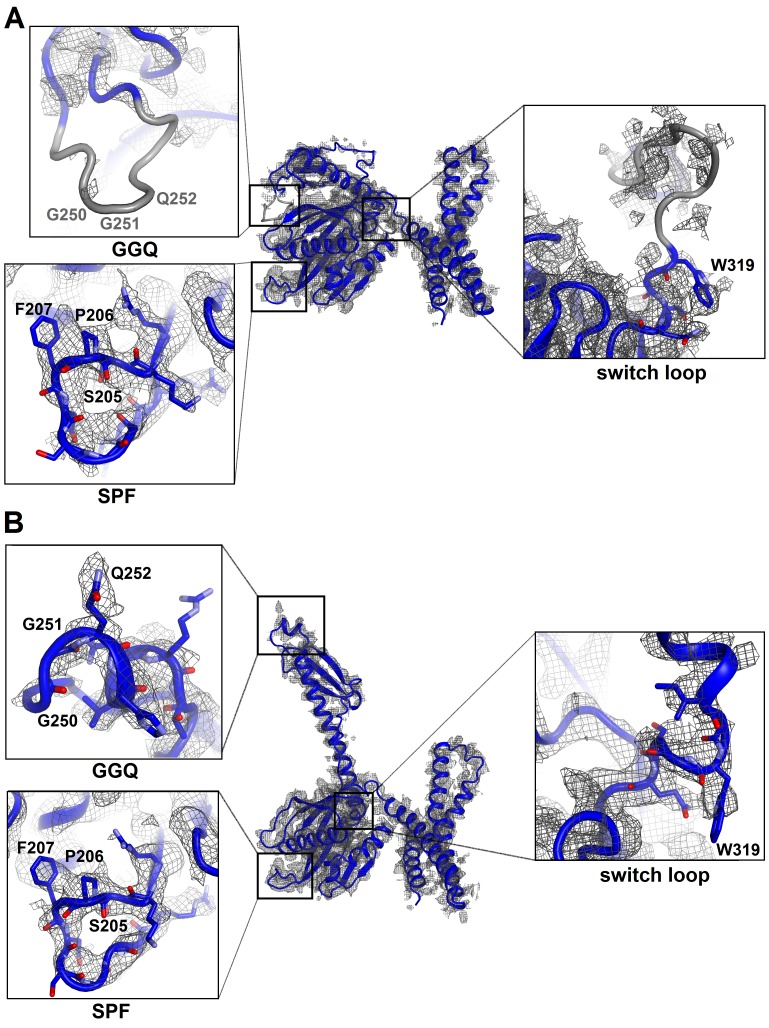
Figure 1. 3.2 Å resolution cryo-EM structures of E. coli 70S ribosome bound with ArfA and release factor RF2.
(A) Structure I with RF2 in a compact conformation; (B) Structure II with RF2 in an extended conformation. Domains 2 and 3 and the GGQ motif of RF2 are labeled. (C) and (D) A close-up view down the mRNA tunnel, showing RF2 and ArfA in the A site of Structure I (C) and Structure II (D). The body and head domains of the 30S subunit are labeled. (E) Extended β-sheet formed by ArfA (red model) and RF2 (blue model). Cryo-EM map (gray mesh) is shown for Structure II at σ = 2.5. (F) Peptidyl-transferase center bound with the 250GGQ252 motif of RF2 in Structure II. Cryo-EM map (gray mesh) is shown at σ = 2.5 for RF2 and at σ = 4.5 for 23S ribosomal RNA and the 74CCA76 end of the P-site tRNA. The maps were sharpened by applying the B-factor of −120 Å2. Additional views of cryo-EM density are available in Figure 1—figure supplements 1–5. In all panels, the large 50S ribosomal subunit is shown in gray/light-blue; the small 30S subunit in yellow; mRNA in green; E-site tRNA in magenta; P-site tRNA in orange; ArfA in red and RF2 in blue.