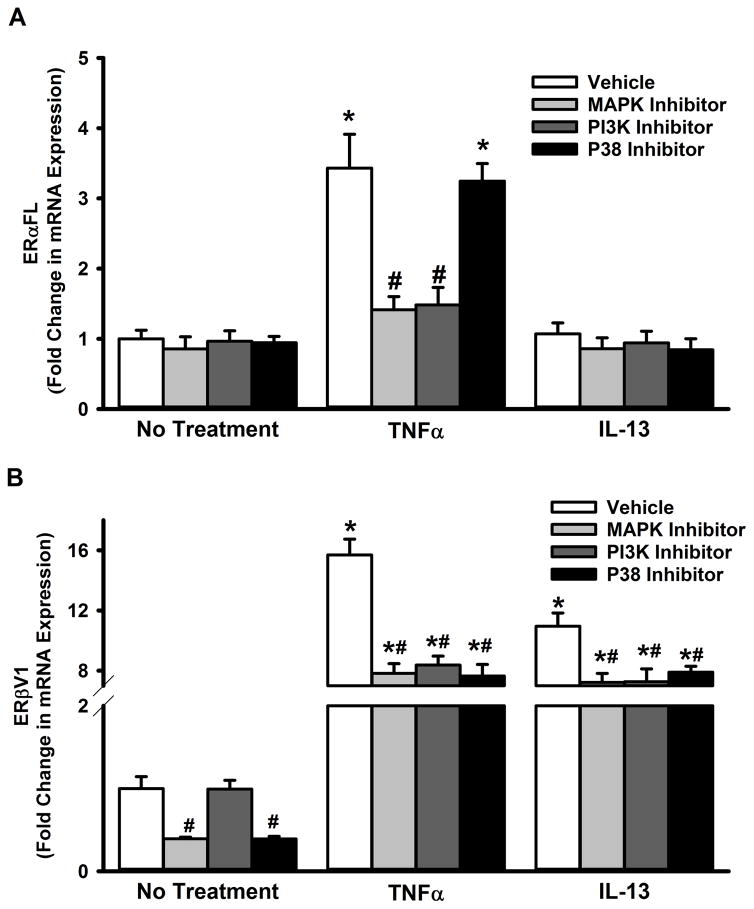
Figure 7. Inflammation-associated cytosolic signaling cascades regulate ERα and ERβ expression in the ASM.
Non-asthmatic ASM cells were treated with pharmacological inhibitors of P38, MAPK42/44 or PI3K pathways: MAPK42/44 was inhibited with 2μM PD98059, PI3K with50nM Wortmannin, and P38 with 600nM SB203580. After 2h, cells were exposed to either 20ng/ml TNFα or 50ng/ml IL-13 for 48h before total RNA was isolated and reverse transcribed. The resultant cDNA was subjected to qPCR to measure the expression of full-length ERα (ERα-FL) or ERβ variant 1. (A) None of the inhibitors caused a change in the basal expression of ERα-FL. While inhibiting either MAPK(42/44) or PI3K pathway resulted in a significant reduction in TNFα-induced surge in ERα-FL expression, blocking the P38 pathway had no effect. IL-13 does not seem to affect ERα-FL expression, in the presence or absence of inhibitor drugs. (B) However, all three pathways tested (MAPK(42/44), PI3K and P38) seem to regulate TNFα or IL-13-mediated effects on ERβ expression: inhibiting any of these signals decreases both TNFα- and IL-13-induced augmentation of ERβ-V1 levels. N=4, each group; *indicates significant difference from vehicle; ‘No Treatment’ control; #indicates significant difference between the vehicle and the TNFα/ IL-13-treated groups; P<0.05.