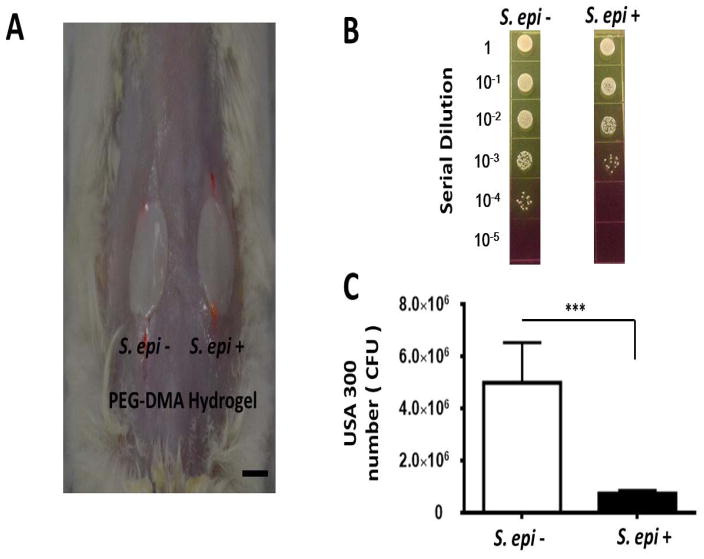
Figure 6.
(A) Suppression of USA300 growth in skin wounds by S. epidermidis-laden PEG-DMA hydrogels. The PEG-DMA hydrogels with (S. epi +) or without (S. epi −) S. epidermidis were applied over the wounded sites made on the dorsal skin of the ICR mice 10 min after application of USA300 (106 CFU/1 μl PBS). Scale bar=1.0 cm. (B) Twenty four h after bacterial application, bacterial CFUs in the wound were counted by plating serial dilutions (1:100–1:105) of the wound homogenates on phenol-red supplemented MSA plates. (C) The CFUs of USA300 (yellow colonies) were displayed as the mean ± SD of three separate experiments with 3 mice per group in each experiment. ***P<0.001; two-tailed t-tests.