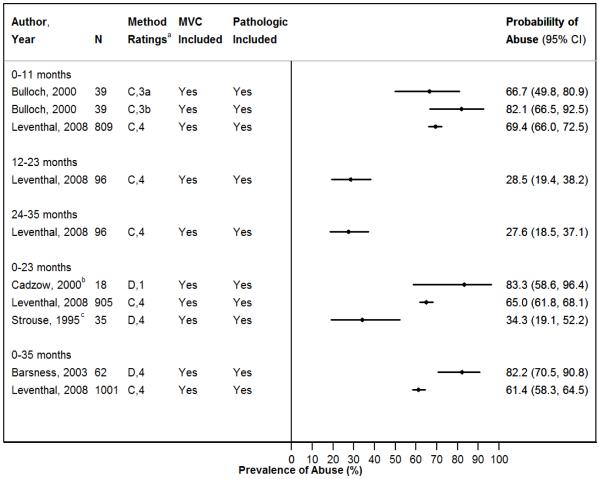
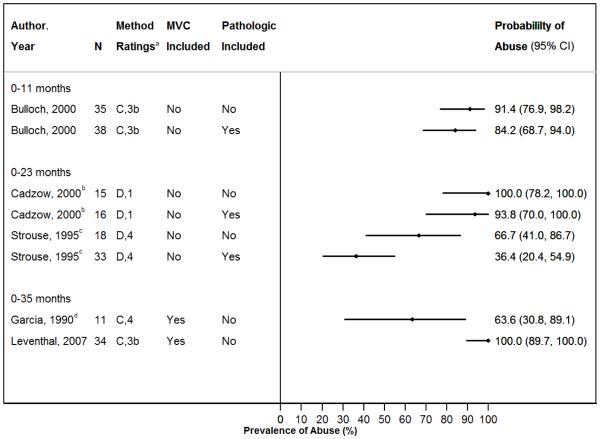
Figure 2. A & B - Probability of Abuse in Children with Rib Fractures.
A. All Children with Rib Fractures (All Etiologies Included)
Proportion of cases with abusive rib fractures in included studies, grouped by subject age. Ribs fractures caused by MVCs and pathologic diseases were included in the denominator in calculating prevalences.
Abbreviations: MVC=motor vehicle crash; n=sample size; CI=confidence interval.
aPresents overall study methodology ranking (A-D) and abuse determination methodology ranking (1-5).
bThe majority of subjects in this study were <12 months old.
cStudy inclusion criteria included children up to 4 years old, but all subjects were 0-24 months old.
B. Restricted Cohorts Excluding Children with MVC-related Rib Fractures and/or Pathologic Rib Fractures
Proportion of cases with abusive rib fractures in included studies with restricted cohorts, grouped by subject age.
Abbreviations: MVC=motor vehicle crash; n=sample size; CI=confidence interval.
aPresents overall study methodology ranking (A-D) and abuse determination methodology ranking (1-5).
bThe majority of subjects in this study were <12 months old.
cStudy inclusion criteria included children up to 4 years old, but all subjects were 0-24 months old.
dThis assumes that all 7 children with rib fractures due to child abuse were <36 months old according to the statistics reported. The authors do not report a clear breakdown by age.