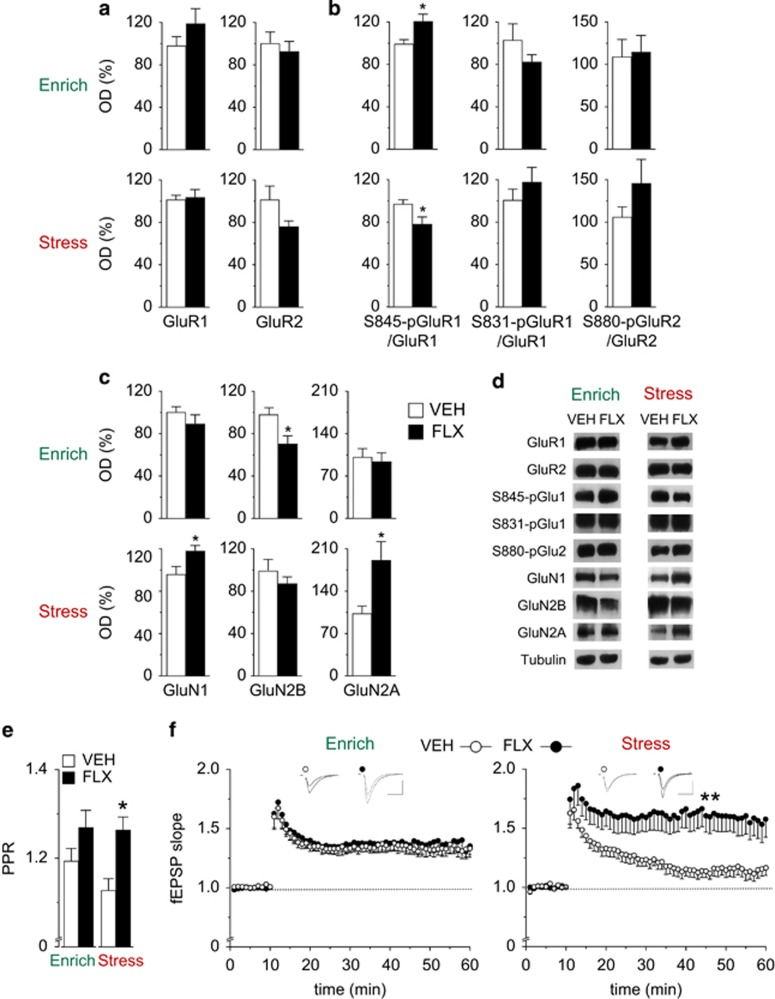
Figure 4.
Fluoxetine (FLX) modifies molecular and cellular correlates of synaptic plasticity in an environment-dependent manner. (a) Hippocampal levels of AMPA receptor subunits GluR1 and GluR2, and (b) their phosphorylation measured by western blotting. FLX induced opposite effects on GluR1 phosphorylation at Ser 845 according to the quality of the environment. (c) Hippocampal levels of NMDA receptor subunits GluN1, GluN2A and GluN2B measured by western blotting. (d) Representative western blots. n=8 for all groups in western blot analyses. Data shown as mean±s.e.m. of the control. *P<0.05 vs respective vehicle (VEH) group. (e) FLX increased paired-pulse ratio in the stressful condition but had no effect in the enriched condition. VEH: n=18/5; FLX: n=15/4. (f) FLX affect CA1 plasticity in mice exposed to stress condition. In the enriched condition, both FLX and VEH mice developed a robust LTP 45 min after stimulation (single 100 Hz burst; VEH: n=12/5; FLX: n=11/5). In the stressful condition, FLX mice showed a remarkable increase in the LTP amplitude compared with VEH (VEH: n=14/6; FLX: n=10/5). Arrows indicate time of application of HFS. fEPSP, field excitatorypostsynaptic potential; PPR, paired-pulse ratio. Data shown as mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs respective VEH group.