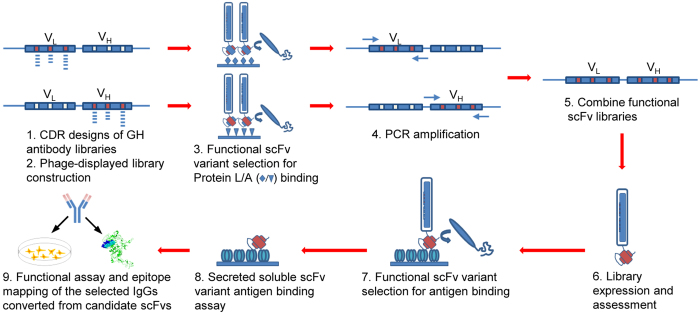
Figure 4. Schematic depiction of the construction of GH2 synthetic antibody library and the selection of antigen-binding GH2 antibodies.
The VH and VL domains of the Av1 scFv template were diversified separately based on the oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis procedure46 (step 1 ~ 2); the 3 CDRs in each of the variable domains were diversified simultaneously46. The scFv template for the library construction is shown in Supplementary Figure S4, and the CDR sequences are encoded in the DNA primer set shown in Supplementary Table S3. More than 109 scFv variants displayed on M13 phage particles were harvested from E. coli cultures for each of the VH and the VL libraries. The properly folded variants of the phage-displayed VH library were selected against Protein A binding; the properly folded variants of the phage-displayed VL library were selected against Protein L binding31,32 (step 3). These selections mimicked the elimination of unstructured BCRs during B cell development. The GH2 library was constructed by PCR-assembling the DNA segments of the well-folded VL variants with the well-folded VH variants (step 4 ~ 5)34; more than 109 scFv variants of the GH2 library were expressed on M13 phage particles (step 6). The phage-displayed GH2 scFvs were mostly well folded: around half of the randomly selected E. coli colonies, each harboring single phagemid, can display well-folded scFv on phage surface and secret in culture free soluble scFv binding to both Protein L and Protein A. The scFv binders against HER2/ECD were selected in two to three selection/amplification cycles from the phage-displayed GH2 scFv library with the standard phage display selection/screening procedure31,32 (step 7). Candidate scFvs were then screened for soluble scFv binding to HER2/ECD (step 8). Selected scFvs were converted into IgGs for functional assay and epitope mapping (step 9). Detailed experimental procedures are described in Methods.