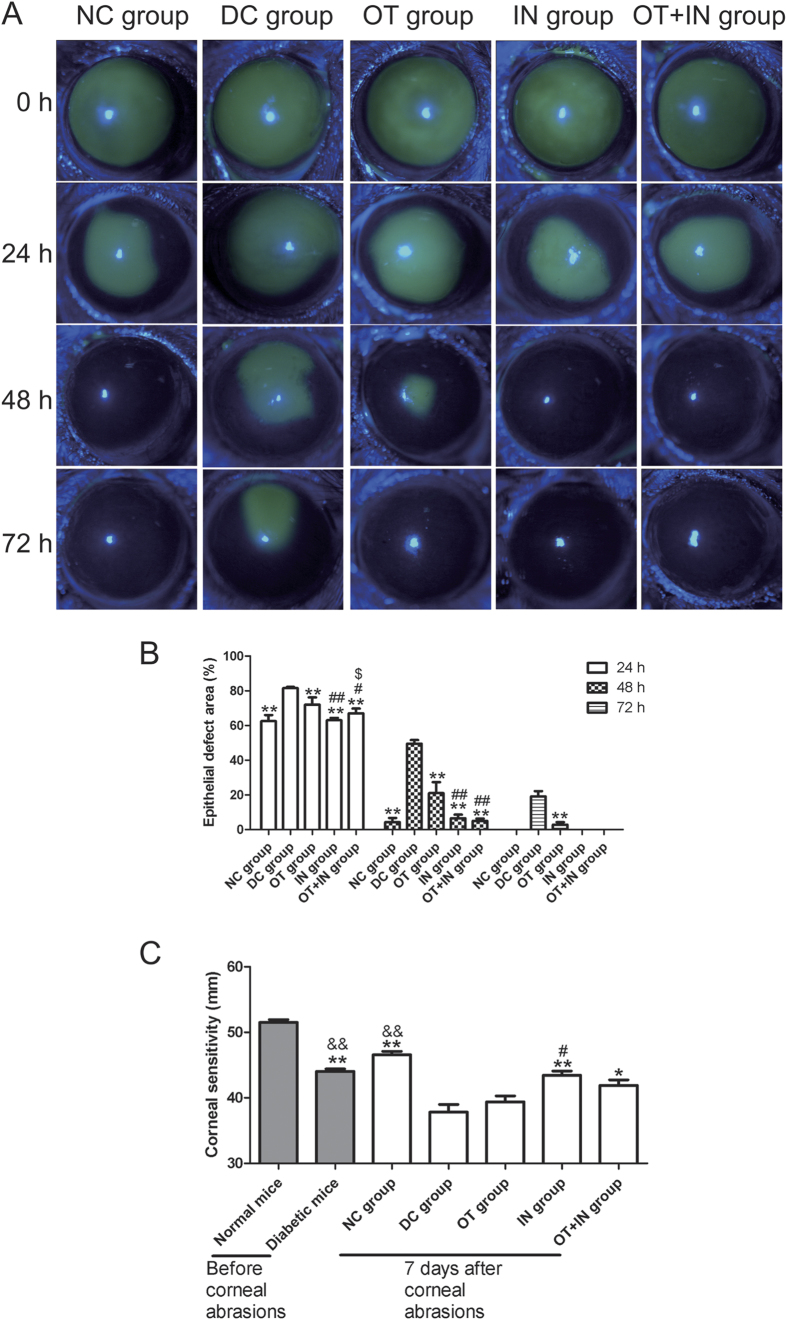
Figure 1. Nanomicelle curcumin promotes corneal epithelial wound healing and sensitivity recovery in diabetic mice.
The effect of 7-day treatment with topical and/or intranasal nanomicelle curcumin in promoting diabetic corneal epithelial wound healing after corneal epithelium abrasion was investigated. (A) The corneal epithelial healing rate was significantly different from 24 h after corneal epithelium abrasion. (B) The corneal epithelial defect significantly decreased in diabetic mice treated with nanomicelle curcumin when compared with the DC group mice, and the decrease was similar to that in the NC group mice (**P < 0.01 when compared with the DC group; #P < 0.05, with the OT group; ##P < 0.01, with the OT group; $P < 0.05, with the IN group; n = 6). (C) The attenuated corneal sensitivity in diabetic mice recovered in the nanomicelle curcumin treatment groups (*P < 0.05 when compared with the DC group; **P < 0.01, with the DC group; #P < 0.05, with the OT group; ##P < 0.01 with the OT group; &&P < 0.01, with normal mice before corneal epithelium abrasion; n = 6).