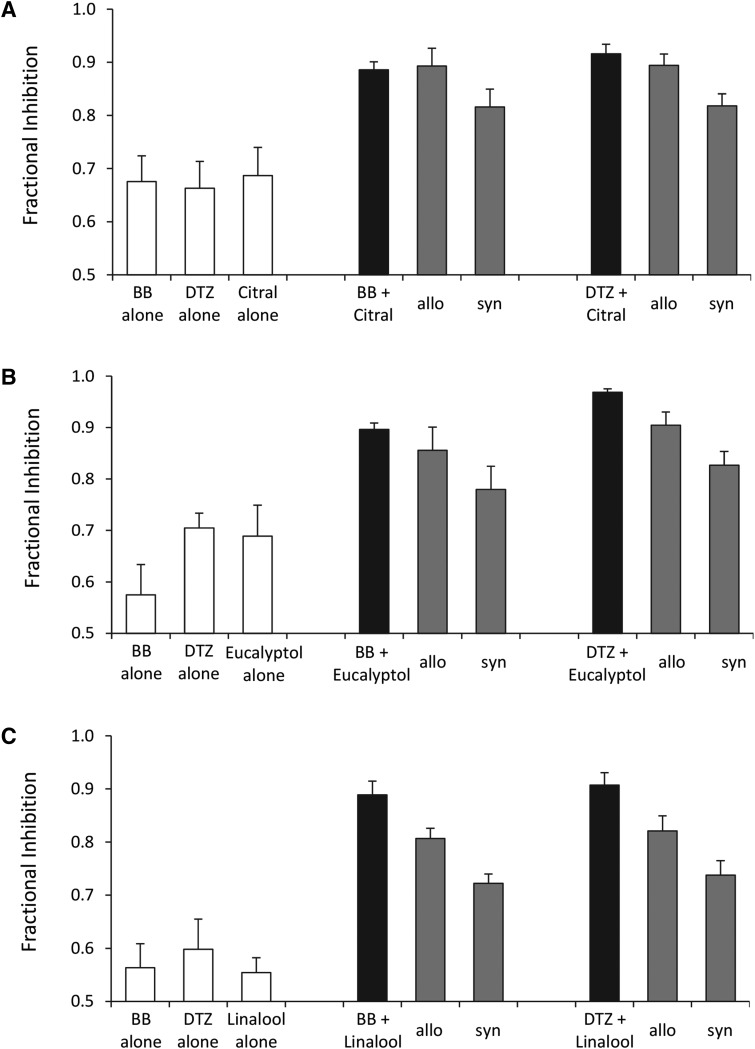
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of the 5-HT3 receptor using a dual-application approach. 5-HT3 receptors were activated with a supramaximal (100 µM) concentration of 5-HT. Concentrations of BB, DTZ, and the terpenoids were preselected to inhibit the response by approximately 62% when used alone. Results are shown in the white bars. These same concentrations were then applied in dual combinations, giving results shown in the black bars. The gray bars are the allotopic (allo) and syntopic (syn) predictions based on the levels of inhibition caused by the compounds alone. Data are the mean ± S.E.M. Two-way analysis of variance with Dunnett’s post-hoc test was used (IBM SPSS Statistics 20) to compare actual and predicted dual application responses. (A) Citral (n = 7). For BB, P = 0.019 (analysis of variance), P = 0.95 (H0: BB+citral = allo), P = 0.031 (H0: BB+citral = syn); and for DTZ, P = 0.0005 (analysis of variance), P = 0.42 (H0: DTZ+citral = allo), P = 0.0004 (H0: DTZ+citral = syn). (B) Eucalyptol (n = 6). For BB, P = 0.015 (analysis of variance), P = 0.38 (H0: BB+eucalyptol = allo), P = 0.009 (H0: BB+eucalyptol = syn); and for DTZ, P = 0.00008 (analysis of variance), P = 0.013 (H0: DTZ+eucalyptol = allo), P = 0.00004 (H0: DTZ+eucalyptol = syn). (C) Linalool (n = 5). For BB, P = 0.0006 (analysis of variance), P = 0.023 (H0: BB+linalool = allo), P = 0.0004 (H0: BB+linalool = syn); and for DTZ, P = 0.003 (analysis of variance), P = 0.056 (H0: DTZ+linalool = allo), P = 0.002 (H0: DTZ+linalool = syn). In all experiments, stable levels of inhibition were achieved by applying the compounds for 1 minute before 5-HT was added.