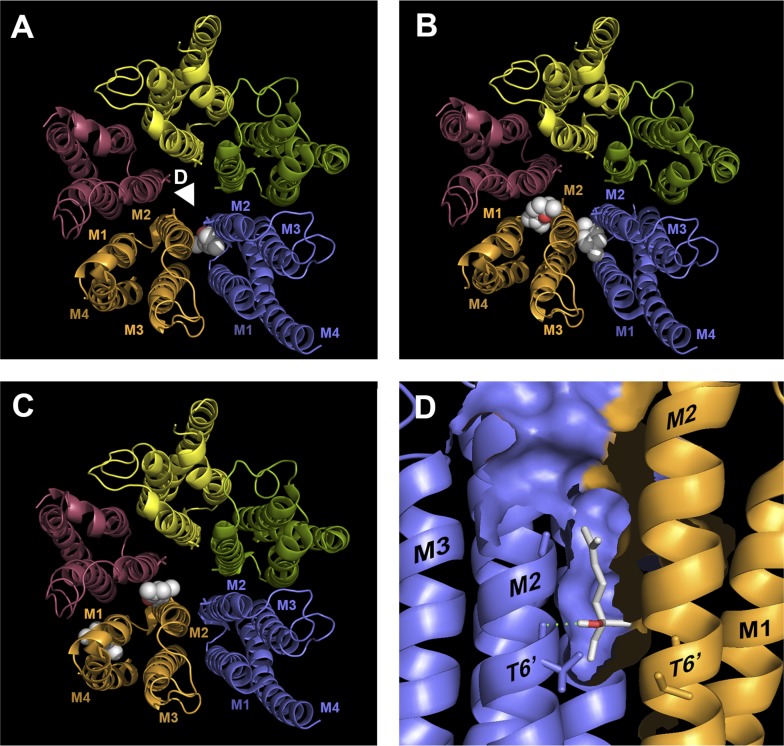
Fig. 7.
Predicted binding locations for citral, eucalyptol, and linalool in a homology model of the human 5-HT3 receptor. Using a loosely defined binding site (see Materials and Methods), 10 docked poses were generated for each ligand. Examples from the docked pose clusters (sphere representation) are shown at each of the predicted binding sites. The transmembrane domains of the five subunits that form the functional 5-HT3 receptor are shown as different colored ribbons viewed from the extracellular side, with both the intracellular and extracellular domains removed for clarity. (A) A single binding site was predicted for linalool with the docked pose cluster differing by only 2.29 Å root-mean-square deviation. The white arrowhead indicates the origin from which (D) is viewed. (B) Two sites were predicted for eucalyptol, but were similarly located at the boundaries of adjacent subunits. (C) For citral, two potential binding sites were identified, a major (6/10) site at the interface of adjacent subunits and a minor site located at the lipid-exposed interface at the intracellular ends of M1 and M4. (D) In four of the 10 docked poses for linalool, PyMol 1.3 predicted hydrogen bonds (blue dotted line) between the ligand’s terminal hydroxyl and the backbone of the channel-lining 6' Thr residue.