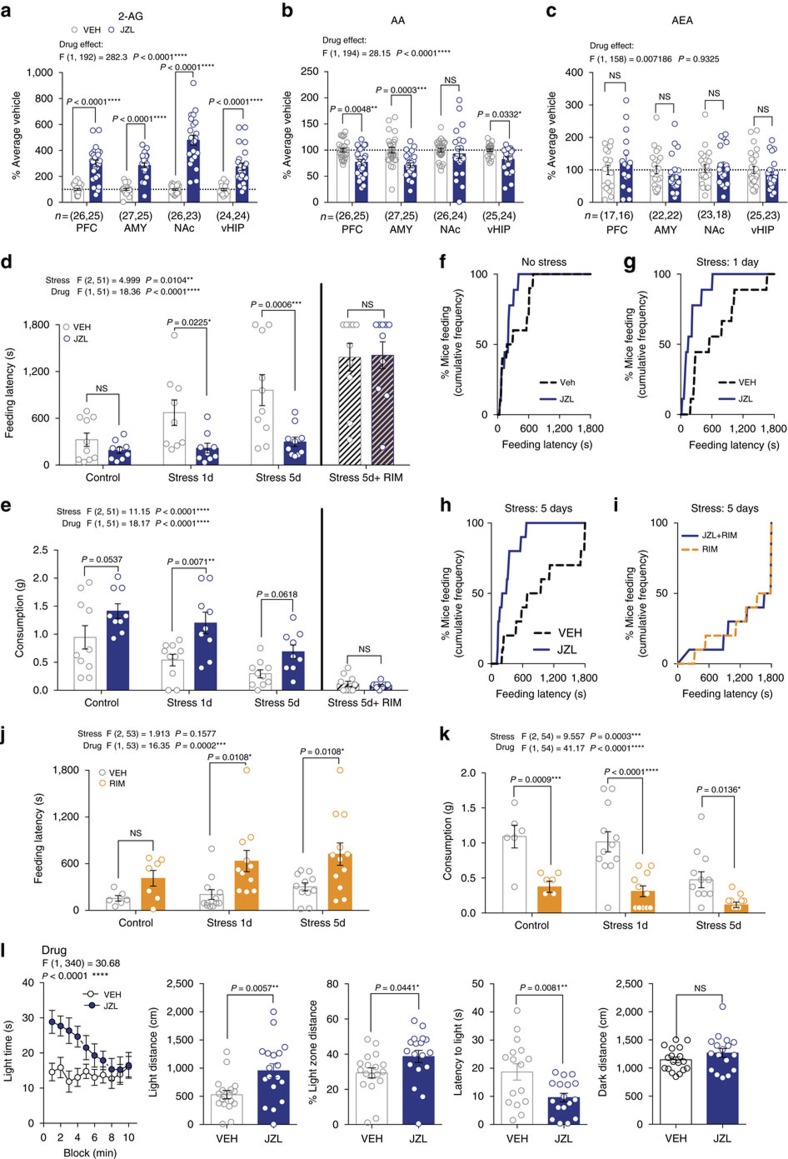
Figure 1. Modulation of stress-induced anxiety-like behaviour by 2-AG signalling.
(a–c) Effects of JZL-184 (8 mg kg−1; blue) on 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), arachidonic acid (AA), and anandamide (AEA) in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), amygdala (AMY), nucleus accumbens (NAc), and ventral hippocampus (vHIP). Data combined from two independent experiments. (d,e) Effects of JZL-184 treatment on feeding latency (top) and consumption (bottom) in the novelty-induced hypophagia test (NIH) without stress, after 1 or 5 days of foot-shock stress, and after 5 days of stress in combination with the CB1R inverse agonist Rimonabant (RIM; 1 mg kg−1). (f–i) Cumulative feeding latency distributions of vehicle and JZL-184-treated mice without stress, after 1 or 5 days of foot-shock stress, and after 5 days of stress in combination with Rimonabant. (j,k) Effects of Rimonabant (orange) on feeding latency and consumption in NIH without stress, and after 1 and 5 days of foot-shock stress. (i) Effects of JZL-184 treatment in the light-dark box test after 1 day of foot-shock stress. F and P values for two-way ANOVA shown above (a–e,j–l). P values shown for pairwise comparisons derived from Holm-Sidak multiple comparisons test after ANOVA or unpaired two-tailed t-test (l). Data are presented as mean±s.e.m.