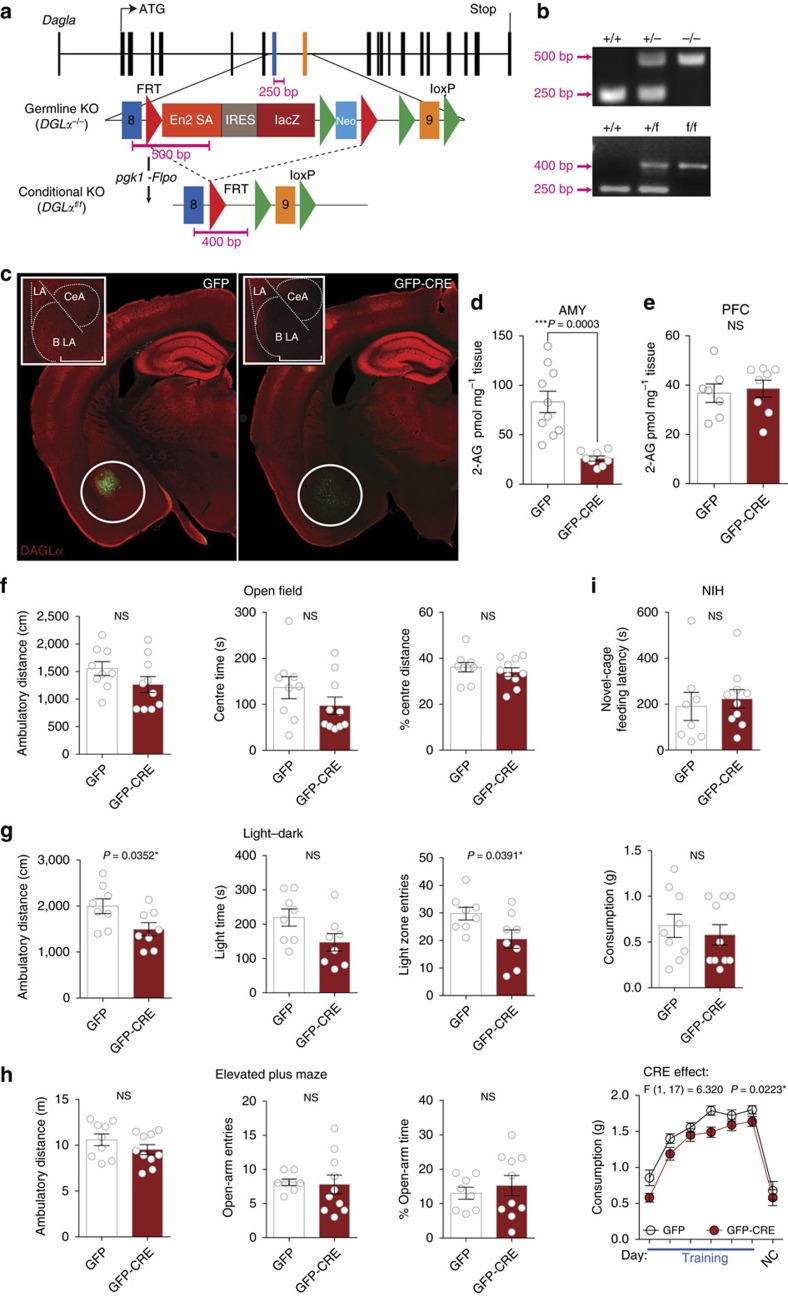
Figure 6. Conditional DAGLα knockout mice and BLA-specific DAGLα deletion.
(a) Diagram of targeting construct and strategy for the generation of DAGLαf/f mouse. Mice harboring dagla gene-trap cassette16 were crossed to pgk-Flpo mice to generate conditional knockouts with loxP sites flanking exon 9. (b) PCR products for genotyping of germline (DAGLα−/−) and conditional (DAGLαf/f) knockouts. Primer binding sites shown in a. (c) Representative coronal brain slices from DAGLαf/f mouse after BLA-AAV-GFP (left) and BLA-AAV-GFP-CRE (right) injection, and 20X magnification of BLA-DAGLα immunoreactivity of BLA-GFP control and BLA-GFP-CRE injected mice (square insets). White circles represent typical brain punch dissections for mass spectrometry. Inset scale bars are 500 μm. (d) Amygdala 2-AG levels after AAV-GFP and AAV-GFP-CRE BLA-injection from punch biopsies as indicated by white circles in c. (e) PFC 2-AG levels after BLA-AAV-GFP and BLA-AAV-GFP-CRE injection. (f) Effect of AAV-GFP vs. AAV-GFP-CRE BLA-injection on behaviour in open-field, (g) light-dark box, and (h) elevated plus-maze. (i) Effect of AAV-GFP vs. AAV-GFP-CRE BLA-injection on baseline novelty-induced hypophagia (NIH) testing. P values shown for unpaired one-tailed t-test above each d–i. F and P values for two-way ANOVA shown in i. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m.