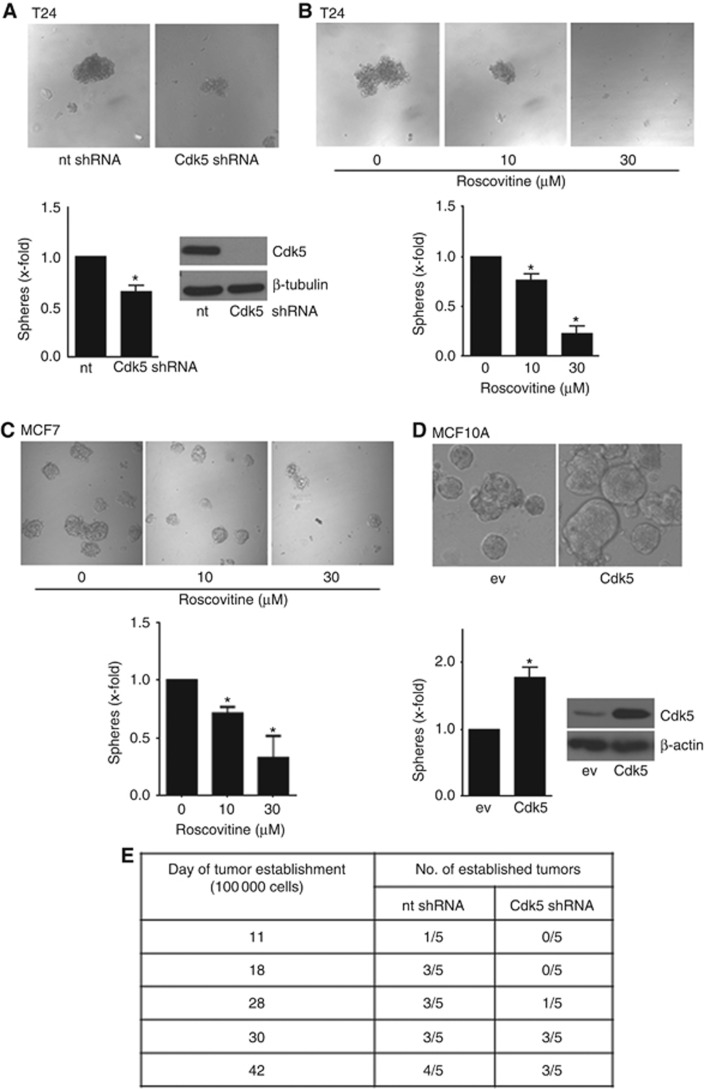
Figure 4.
Cdk5 regulates sphere formation and tumour establishment.(A) Tumorsphere formation of non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 shRNA T24 cells is shown (mean±s.e.m., *P<0.05, n=3). Immunoblots of non-targeting (nt) or Cdk5 shRNA-transduced T24 cells for Cdk5 and β-tubulin (loading control) proof Cdk5 knockdown. (B) Tumorsphere formation after pretreatment of T24 cells with roscovitine for 24 h before resuspension in fresh sphere-formation medium and cultivation for further 10 days in presence of roscovitine is shown (mean±s.e.m., *P<0.001, n=3). (C) Tumorsphere formation after pretreatment of MCF7 cells with roscovitine for 24 h before resuspension in fresh sphere-formation medium and cultivation for further 10 days in presence of roscovitine is shown (mean±s.e.m., *P<0.05, n=3). (D) Sphere formation of non-tumorous MCF10A cells overexpressing empty vector (ev) or Cdk5/p35 (Cdk5) is shown (mean±s.e.m., *P<0.05, n=3). The immunoblot of MCF10A cells overexpressing either empty vector (ev) or Cdk5/p35 (Cdk5) for Cdk5 and β-actin (loading control) proofs Cdk5 overexpression. (E) Cdk5 inhibition impairs tumor establishment in vivo. The tables indicate the time of tumour establishment and the number of established tumours of mice injected with non-targeting (nt) shRNA and Cdk5 shRNA tumour cells (1 × 105 cells).