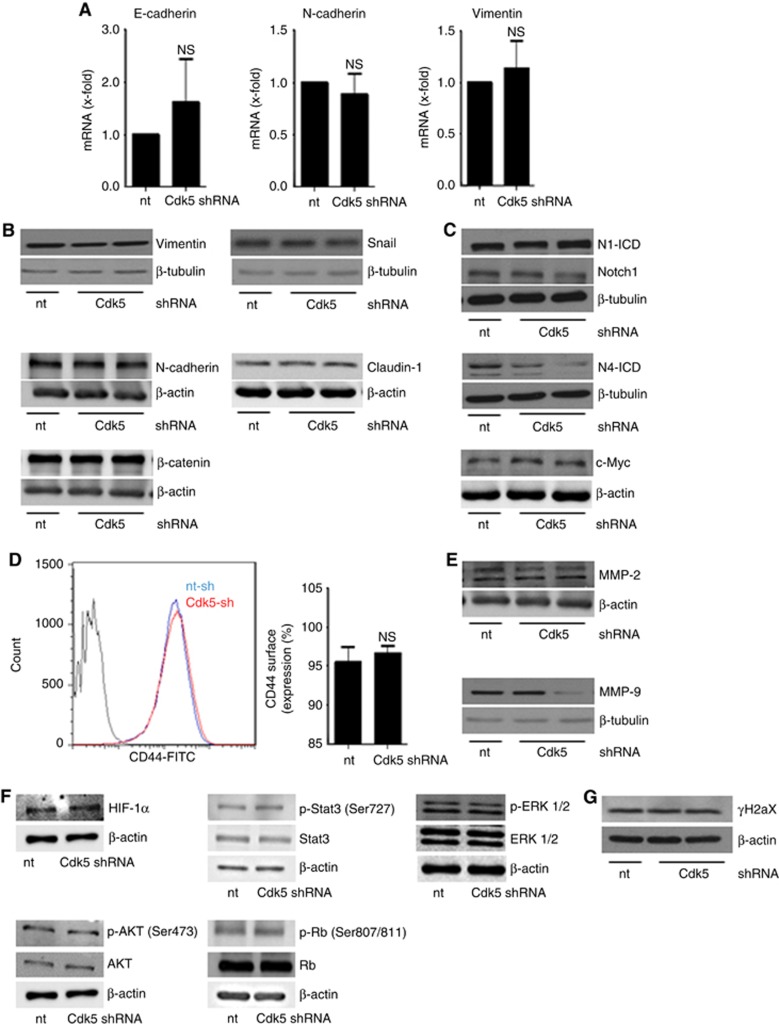
Figure 5.
Cdk5 knockdown does neither affect EMT related signalling nor common cell survival pathways or DNA damage.(A) Bar graphs show mRNA levels of the EMT markers E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin in non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 shRNA-transduced cells (n=3). (B) Immunoblots show protein levels of the EMT markers vimentin, snail, β-catenin, N-cadherin and claudin-1 from non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 shRNA cells. β-actin and β-tubulin indicate equal loading. (n=3). (C) Immunoblots for Notch1 and Notch4 intracellular domain (N1-ICD, N4-ICD) and the Notch downstream target c-Myc in non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 knockdown cells are shown. β-actin and β-tubulin indicate equal loading. (n=3). (D) Histogram plot from FACS analysis from CD44 surface expression is shown. Bars represent quantification of CD44-positive cells in non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 shRNA cells (mean±s.e.m., NS=not significant, n=3). (E) MMP-2 and MMP-9 immunoblots are shown. β-actin and β-tubulin indicate equal loading. (n=3). (F) Immunoblots show different proteins related to cell survival in non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 shRNA cells. HIF1α, total and phosphorylated Stat3 (S727), ERK1/2, AKT (S473) and Retinoblastoma protein (807/811) are shown. β-actin indicates equal loading (n=3). (G) The immunoblots show phospho-histone H2aX (γH2aX) in non-targeting (nt) and Cdk5 shRNA cells. β-actin indicates equal loading (n=3).