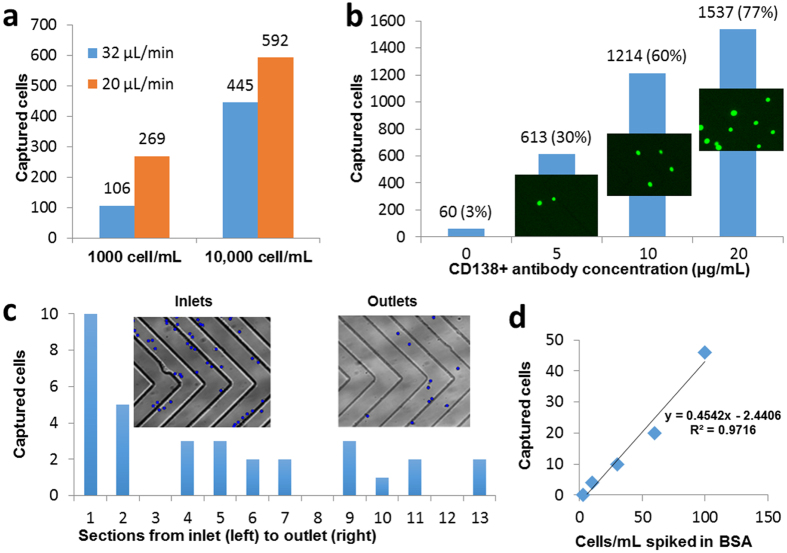
Figure 2. Optimization of the microfluidic device for plasma cell capture.
(a) Effect of sample flow rate and cell concentration on the capture of plasma cells indicates higher capture efficiency at the lower flow rate and lower cell concentration (1 mL of 1000 or 10000 cells/mL in PBS buffer with 1% BSA; 5 μg/mL anti-CD138 antibody). (b) Effect of functionalization of the microfluidic channels with different anti-CD138 antibody concentrations (1 mL of 2000 cells/mL; 20 μL/min). Insets show representative fluorescence images of the captured cells. (c) Cell capture distribution within the channels shows an exponential decrease along the channel. Insets show bright-field images of the channels near the inlet and outlet. Captured cells were manually marked with blue dots, using ImageJ software, for enhanced visualization. (d) The number of cells captured from 1-mL samples with very low concentrations of spiked cells (1 mL of 3, 10, 30, 60, 100 cells/mL) varies linearly with nominal cell concentration.