Fig. 6.
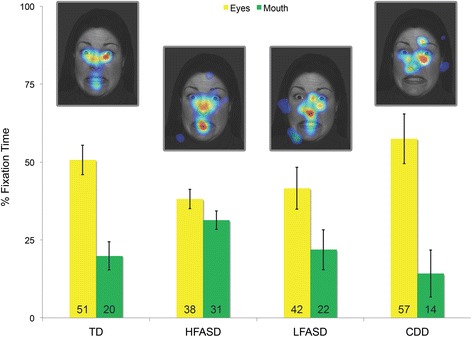
Behavioral analysis through eye tracking. The yellow and green bars of the graph represent the mean % of time spent fixating (y axis) on the eyes and mouth of the faces, respectively, by cohort (x axis): TD (n = 14), HFASD (n = 32), LFASD (n = 7), CDD (n = 5). The gaze heat maps illustrate the group-level gaze data overlaid on one of the images at which subjects looked. Compared to TD subjects, HFASD subjects show decreased fixation on the eyes [t(44) = -2.28, P = 0.03, Cohen’s d = 0.77] and increased fixation on the mouth [t(44) = 2.16, P = 0.04, Cohen’s d = 0.76]. The % of time subjects with LFASD spent looking at the eyes did not differ from HFASD [t(37) = 0.43, P = 0.67, Cohen’s d = 0.17], but CDD subjects fixated eyes significantly more than HFASD [t(35) = 2.19, P = 0.04, Cohen’s d = 1.08]. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. All P values were calculated by independent t test and are two-tailed
