Fig. 1.
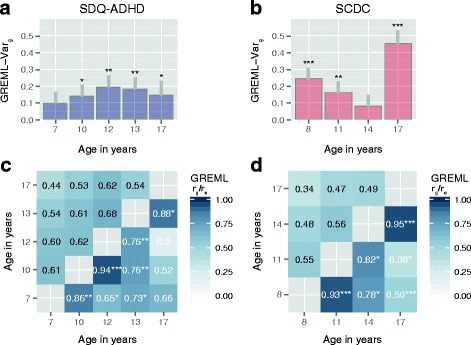
Genetic architecture of SDQ-ADHD and SCDC scores. Genetic-relationship-matrix restricted maximum likelihood (GREML) genetic variance (Varg), genetic (r g) and residual correlations (r e) are shown for SDQ-ADHD scores (a, c) and SCDC scores (b, d) in ALSPAC; grey bars (a, b) indicate one GREML-h2 standard error; r g estimates for each trait (b, d) are shown in the lower triangle, r e estimates (b, d) in the upper triangle. ALSPAC Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children, SCDC Social and Communication Disorders Checklist at 8, 11, 14 and 17 years (rank-transformed), SDQ-ADHD ADHD subscale of the Strength and Difficulties Questionnaire at 7, 10 12, 13 and 17 years (rank-transformed); note that for rank-transformed traits, estimates of SNP-h2 are equivalent to estimates of Varg, as the phenotypic variance has been standardised to one. r g p values: *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01 and ***p ≤ 0.001 (uncorrected for multiple testing, experiment-wise error rate p = 0.01)
