Fig. 1.
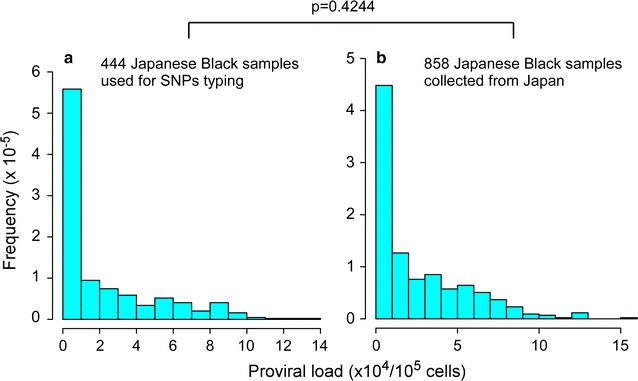
Proviral load estimated from SNP typing of DNA samples from 444 BLV-infected Japanese Black cattle (a) and 858 samples from Japanese Black cattle located in 22 prefectures of Japan (b) [17]. The proviral load in the 444 test samples was representative of the proviral load in Japanese Black cattle nationwide (p value, p = 0.4244; F test). Blood (collected in EDTA-2Na) was obtained from 444 Japanese black cows (aged >4 years), and genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood using the QIAsymphony kit (QIAGEN K.K., Tokyo, Japan). The BLV-CoCoMo-qPCR-2 method (RIKEN genesis, Kanagawa, Japan) was used to measure the BLV proviral load in 676 cattle at a single time-point; of these, 444 were positive for BLV and entered into the association study. Briefly, the BLV long terminal repeat region was amplified using a degenerate primer pair (CoCoMo-FRW and CoCoMo-REV) and an FAM-BLV probe. The BoLA-DRA gene (internal control) was amplified using the primer pair DRA-F and DRA-R and the FAM-DRA probe [31]
