Fig. 4.
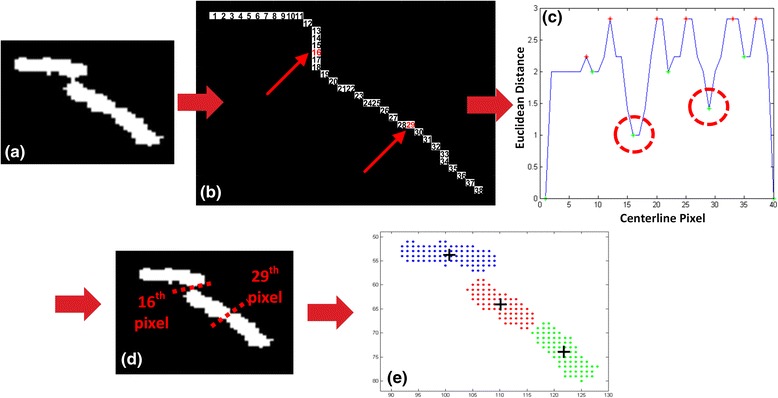
Collinear objects analysis - "Bow ties" identification. a Extracted collinear object. b Skeletonized object with skeleton pixels numbered. The red numbers mark the “bow tie" locations on the centerline. c Distance curve of the object: To construct it we form pairs of opposite-side diametric boundary pixels (w.r.t. the skeleton) and compute their Euclidean distance (local width). Then we search for “deep valleys” (i.e. significant local minima relative to neighboring local maxima (marked with red circles for illustration purposes) and, (d) we split the object at bowtie points (marked by red dashed lines for illustration purposes), that correspond to the deep valley positions in (c). e The collinear object is segmented into three single-cells
