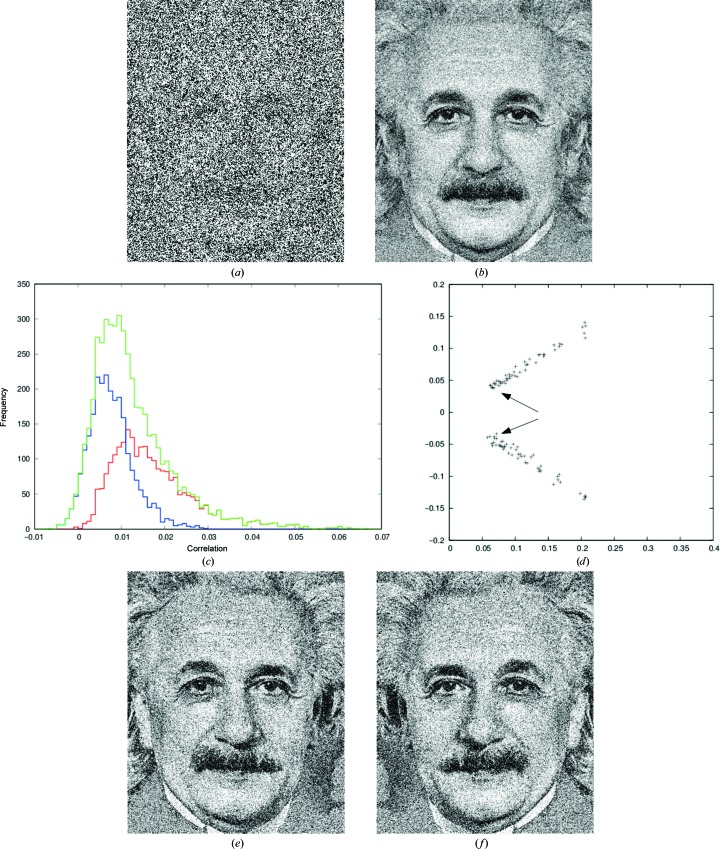
Figure 1.
Portrait of A. Einstein (Wikimedia). (a) Example of portrait with added noise; the signal-to-noise ratio is 1:9. (b) Symmetric result of averaging of noisy images and mirror images. (c) Histograms of correlation coefficients (red, between images of the same type; blue, between images of different types; green, sum of both histograms). (d) Result of two-dimensional analysis: each cross represents one image. Arrows point to images with a 1:13 signal-to-noise ratio. The axes are unitless; only the relevant area of the possible range (a circle with radius 1) is shown. The angle between the two prototypic directions is 65°; its cosine agrees with the correlation of 0.43 between the image and its mirror. (e) The result of averaging the 50 noisy original images; the overall noise level is reduced by averaging. (f) as (e) but for the 50 noisy mirror images