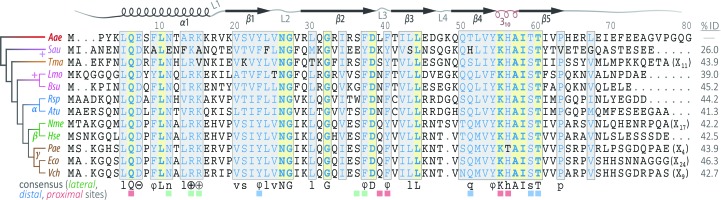
Figure 1.
Multiple sequence alignment of Aae Hfq and some representative homologs. Sequence analysis of several Hfq homologs, characterized from various phyla, reveals the conservation of key amino acids comprising the three distinct RNA-binding regions of Hfq (distal, proximal and lateral). The Aae Hfq sequence is numbered at the top, and secondary-structural elements are drawn based on the Aae Hfq crystal structures reported here; helices are schematized as spirals, strands as arrows and numbered loop labels are shown (a short 310-helix forms loop L5, colored brown). Strictly identical amino acids are in bold blue text on a yellow background, while sites with highly similar residues are highlighted with a gray background; these blocks of partially conserved residues are also lightly boxed. In the consensus sequence shown at the bottom, uppercase letters indicate strict identity and lowercase letters correspond to physicochemically equivalent residues that meet a similarity threshold (≥85% of sites in a given column). Residues known to contact RNA at the proximal, distal or lateral sites are marked with red, blue or green square symbols, respectively. Note the high level of conservation of residues involved in all three RNA-binding sites. In addition to Aae Hfq (from the phylum Aquificae), the 12 aligned sequences include (i) three Hfq homologs from the mostly Gram-positive Firmicutes (Sau, Lmo and Bsu), (ii) a homolog from the ancient phylum Thermotogae and (iii) several characterized Hfq orthologs from the α-, β- and γ-proteobacteria. The relationships between these species are indicated in the dendrogram (left) obtained during the progressive alignment calculation and colored so as to highlight phylum-level differences. The genus/species and sequence accession codes (GenBank) are as follows: Aae, A. aeolicus (AAC06479.1); Sau, Staphylococcus aureus (ADC37472.1); Tma, T. maritima (AGL49448.1); Lmo, Listeria monocytogenes (CBY70202.1); Bsu, Bacillus subtilis (BAM57957.1); Rsp, Rhodobacter sphaeroides (A3PJP5.1); Atu, Agrobacterium tumefaciens (EHH08904.1); Nme, Neisseria meningitidis (P64344.1); Hse, Herbaspirillum seropedicae (ADJ64436.1); Pae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (B3EWP0.1); Eco, Escherichia coli (BAE78173.1); Vch, Vibrio cholerae (A5F3L7.1).