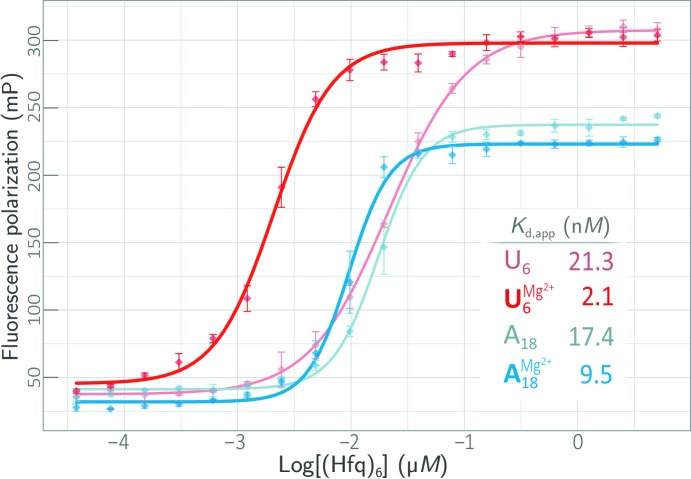
Figure 4.
High-affinity binding of Aae Hfq to A-rich and U-rich RNAs, with variable Mg2+ dependencies. Binding was quantified via fluorescence polarization assays using 5 nM FAM-U6 (red) or FAM-A18 (blue) and varying concentrations of Hfq, either in the absence (thin lines) or presence (thick lines) of 10 mM MgCl2. For each binding reaction, data from three replicates (standard errors given by vertical bars) were fitted using a four-parameter logistic function to model the sigmoidal binding isotherm; nonlinear fits were also performed with an alternative model, accounting for receptor depletion but neglecting cooperativity (§2.4 and Supplementary Fig. S4). The computed binding constants are given (inset) in terms of the (Hfq)6 concentration, as the stoichiometry of all characterized Hfq·RNA complexes, as well as the structural results reported here, suggest that a hexamer is the active/functional unit. The addition of Mg2+ increases the binding affinity for both FAM-U6 and FAM-A18, albeit with a greater influence for the U-rich (proximal site-binding) RNA. Significant binding was not detected for a shorter A-rich (FAM-A6) or C-rich (FAM-C6) ssRNA.