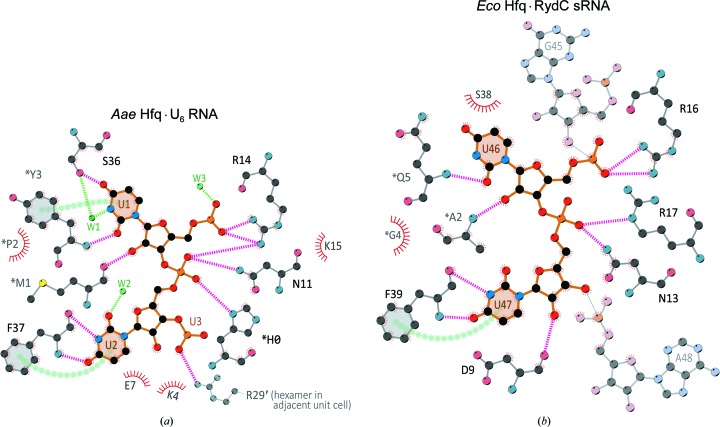
Figure 8.
Conserved pattern of interatomic contacts at the lateral RNA-binding site of Hfq hexamers. In this schematic diagram of the interatomic contacts between the lateral site of Aae Hfq, U6 RNA and nearby H2O molecules (a), protein atoms are shown as ball-and-stick representations (CPK coloring, light gray C atoms) and covalent bonds in the nucleotides are drawn as thicker, orange-colored lines. For clarity, only a subset of H2O molecules is drawn (green, labeled ‘W#’). Here, asterisks denote another Hfq chain in the same unit cell and the prime symbol denotes a neighboring cell. Hydrogen bonds are magenta for protein⋯RNA interactions, while those to H2O are shown in green. Stacking interactions between the aromatic entities φ1 and φ2 are indicated by green circles from φ1⋯φ2. Two nucleotides of uridine (labeled) appear in an open, bridging conformation with the α-helix and β2 strand of an Hfq monomer (gray flanking regions). The phosphate groups are hydrogen-bonded to Asn11 and Arg14 of the N-terminal α-helix, while the nucleobase hydrogen bonds to the backbone atoms of strand β2 (specifically, Ser36 and Phe37), thus imparting specificity for uridine. Note that additional π-stacking interactions are present between the side chain of Phe37 and RNA base U2, as well as within the RNA (between U2⋯U1; not shown for clarity). The lateral pocket of Eco Hfq is shown in (b), complexed with the sRNA RydC [same coloring scheme and conventions as in (a)]. The U46 and U47 bases adopt conformations similar to those seen in (a), with the phosphate groups contacting residues of the α-helix. Phe39 π-stacks with U47, analogous to the interaction seen in Aae Hfq. Note that the adjacent G45 and A48 bases are flipped away from the pocket and are shown here to offer context in the overall sequence of the sRNA. While not strictly conserved in terms of precise amino-acid sequence, the N-terminal regions of the Aae and Eco Hfq homologs do provide similar backbone interactions with U1 and U46, respectively. Note also the directionality of the RNA backbone, which follows the same 5′→3′ path along the lateral site on the surface of the Aae and Eco Hfq rings (see also Figs. 7 ▸ a and 7 ▸ b).