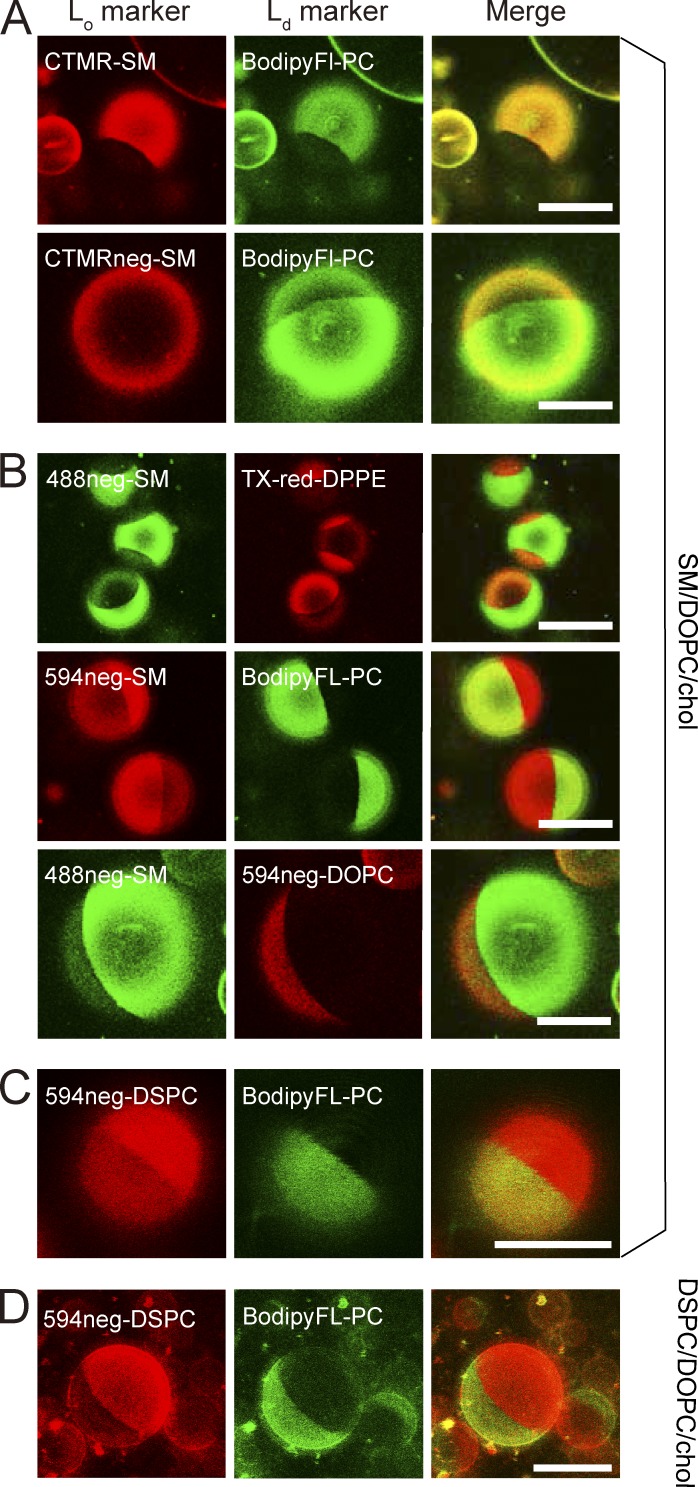
Figure 2.
Partitioning of various fluorescent SM, DSPC, and DOPC analogs into Lo versus Ld domains in phase-separated GUV membranes at 28.5°C, observed by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Phase-separated GUVs consisting of ternary mixtures of SM(18:0)/DOPC/cholesterol and DSPC/DOPC/cholesterol (1:1:1 by moles) were used as host membranes. BodipyFL-PC (green) and Texas-red-DPPE (red) are typical Ld-domain markers. Bars, 20 µm. (A) CTMR-SM, in which CTMR was directly conjugated to the choline headgroup of SM(18:0), preferentially partitions into Lo domains, whereas CTMRneg-SM, in which CTMR was conjugated to the SM headgroup by way of the NEG moiety, partitions almost equally between Lo and Ld domains. The GUVs used consisted of SM/DOPC/cholesterol. (B) Both 488neg- and 594neg-SMs partitioned more into Lo domains than Ld domains, whereas 594neg-DOPC partitioned into Ld domains in phase-separated SM/DOPC/cholesterol-GUVs. (C) In GUVs consisting of SM/DOPC/cholesterol, 594neg-DSPC partitioned more into Lo domains than Ld domains. (D) In GUVs consisting of DSPC/DOPC/cholesterol, 594neg-DSPC preferentially partitioned into Lo domains. See Fig. 3 for the quantitative evaluation of the partitioning behavior.