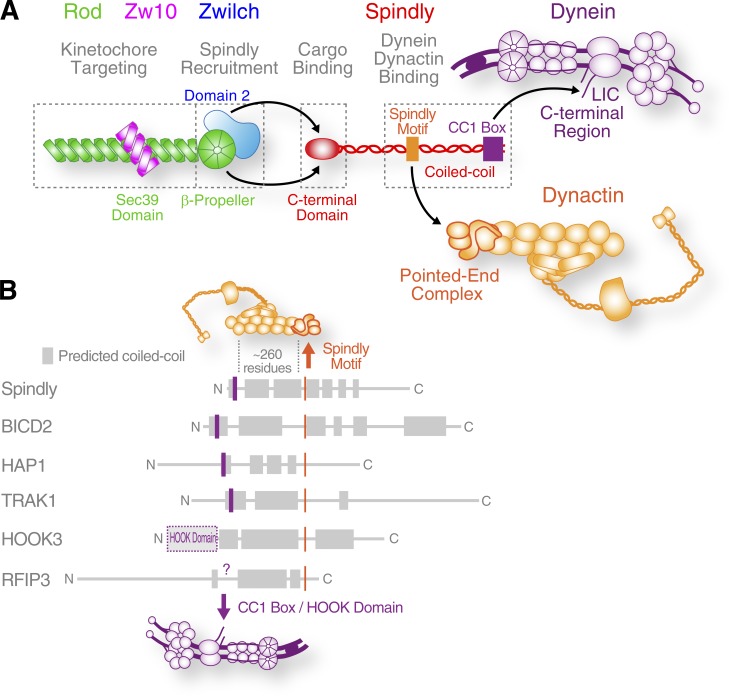
Figure 7.
Molecular interactions implicated in dynein recruitment to kinetochores. (A) Graphic summary of the physical interactions that link the RZZ complex to dynein and dynactin via the adaptor Spindly to recruit the motor to kinetochores. Note that the intact RZZ complex is dimeric but shown here as a monomer for simplicity. (B) Spindly and other dynein adaptors may use a similar mechanism to engage with dynein and dynactin (see Fig. S4 A). Common features include a Spindly-like motif implicated in pointed-end complex binding and an N-terminally located CC1 box for LIC binding. The intervening coiled-coil region likely binds along the Arp1 filament (Urnavicius et al., 2015).