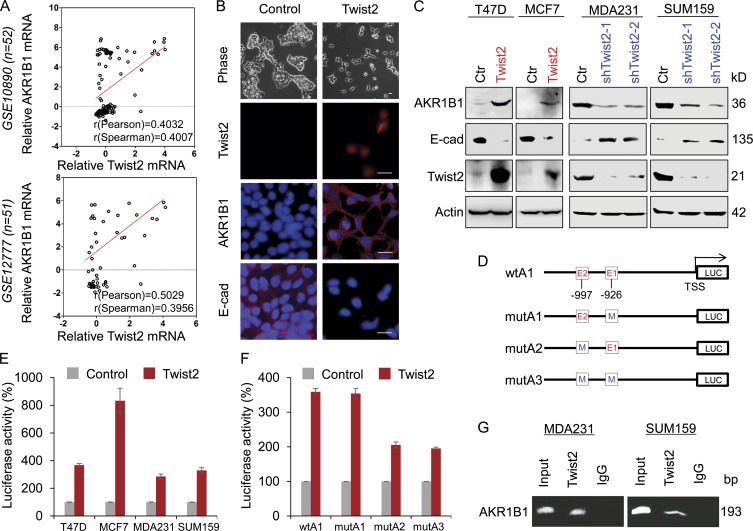
Figure 2.
AKR1B1 positively correlates with Twist2 expression and is a direct transcriptional target of Twist2. (A) Analysis of public datasets (GSE10890 and GSE12777) for the expression of AKR1B1 and Twist2. The relative level of AKR1B1 was plotted against that of Twist2. Correlations were analyzed using Pearson’s correlation method and Spearman’s rank correlation test. (B) Stable clones with empty vector or Twist2 expression were established in T47D cells. Morphological changes indicative of EMT are shown in the phase contrast images. Expression of AKR1B1, E-cadherin (E-cad), and Twist2 was analyzed by immunofluorescent staining. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue). Bar, 20 µm. (C) Expression of AKR1B1, E-cadherin, and Twist2 was analyzed by Western blotting in T47D and MCF7 cells infected with empty vector (Ctr) or Twist2-expressing vector (left), as well as MDA-MB231 and SUM159 cells with stable empty vector or knockdown of Twist2 expression (right). (D) Schematic diagram showing positions of potential Twist2-binding E-boxes in AKR1B1 promoter and AKR1B1 promoter luciferase (LUC) constructs used. E, E-box; M, mutated. (E) AKR1B1 promoter luciferase construct (wtA) was coexpressed with empty vector or Twist2 in T47D, MCF7, MDA-MB231, and SUM159 cells, respectively. After 48 h, luciferase activities were determined and normalized (mean ± SD in three separate experiments). (F) AKR1B1 promoter luciferase construct (wtA1) as well as its E-box mutants (mutA1, mutA2, and mutA3) were coexpressed with empty vector or Twist2 in T47D cells. Luciferase activities were determined and normalized as in E. (G) ChIP analysis for binding of Twist2 to the AKR1B1 promoter in MDA-MB231 and SUM159 cells.