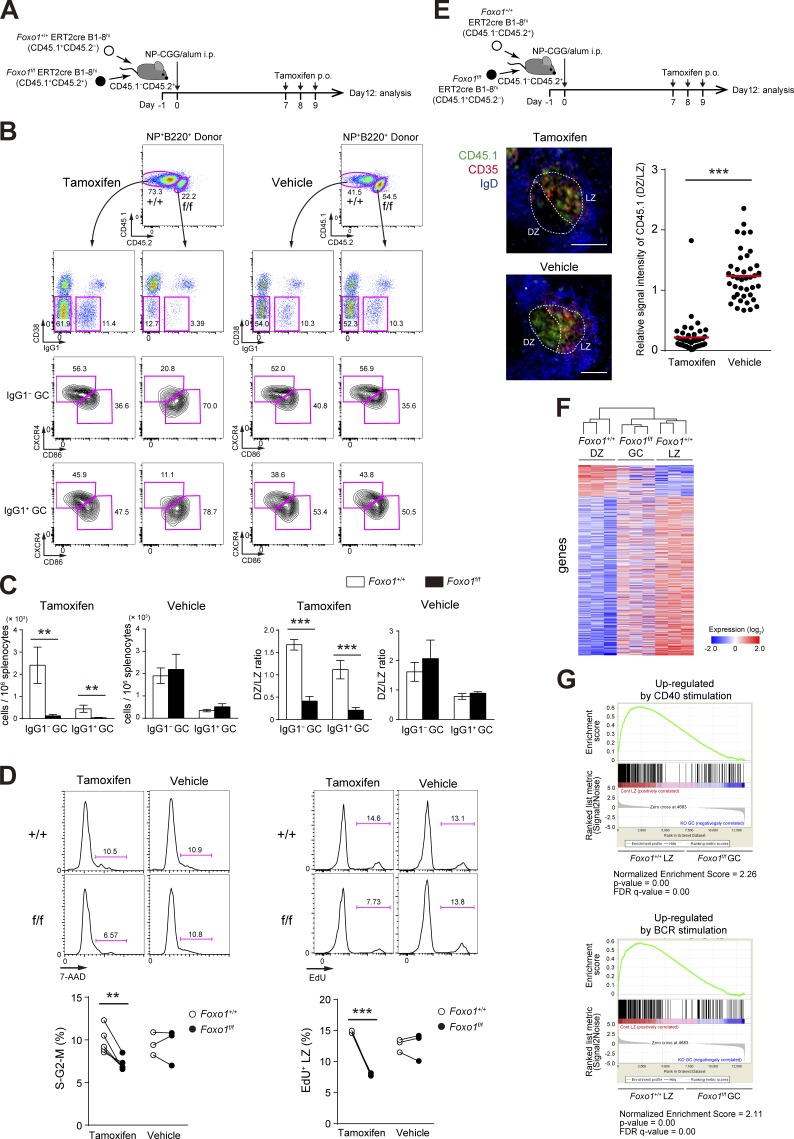
Figure 2.
Foxo1 is required for GC maintenance. (A) Schematic illustration of the experimental protocol for B–D, F, and G. (B) Flow cytometry of NP-specific donor B cells (CD45.1+B220+NP+). (C) Histograms representing the number of donor IgG1− GC B cells (CD45.1+B220+NP+CD38−IgG1−) and IgG1+ GC B cells (CD45.1+B220+NP+CD38−IgG1+) in 106 splenocytes (left), and the ratio of DZ:LZ cells (right). n = 3 biological replicates. (D, left) DNA content measurement of Foxo1+/+ and Foxo1f/f LZ GC B cells assessed by 7-AAD staining. n = 5 and 3 biological replicates for tamoxifen and vehicle treatment, respectively. (right) Proliferation status of Foxo1+/+ and Foxo1f/f LZ GC B cells assessed by EdU incorporation 30 min after an EdU injection. n = 3 biological replicates. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis. (top) Schematic illustration of the experimental protocol. (bottom left) Representative images of immunofluorescence microscopy of spleen sections showing expression of CD45.1 (Foxo1f/f-derived donor cells), CD35 (FDC network), and IgD (follicular B cells). DZ and LZ defined by the presence of CD35+ FDCs are surrounded by dashed lines. Bars, 100 µm. (bottom right) Quantification of relative CD45.1 signal intensity in the DZ compared with that in the LZ. Each symbol represents a single GC, and red bars indicate the mean. n = 43 (tamoxifen) and 40 (vehicle) GC pooled from three animals. (F) Hierarchical clustering of the gene expression profiles of Foxo1+/+ DZ, Foxo1f/f GC, and Foxo1+/+ LZ B cells using genes differentially expressed (more than twofold) between Foxo1+/+ DZ and Foxo1+/+ LZ B cells (normalized log2 values based on RNA-seq analysis). n = 3 biological replicates. (G) Gene set enrichment analysis showing the enrichment for genes up-regulated after ligation of CD40 (top) and BCR (bottom) compared of Foxo1+/+ LZ B cells with Foxo1f/f GC B cells. Error bars represent SD. Data are representative of three (B and C) or two independent experiments (D and E) and from one experiment (F and G). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; unpaired Student’s t test (E) and paired Student’s t test (C and D).