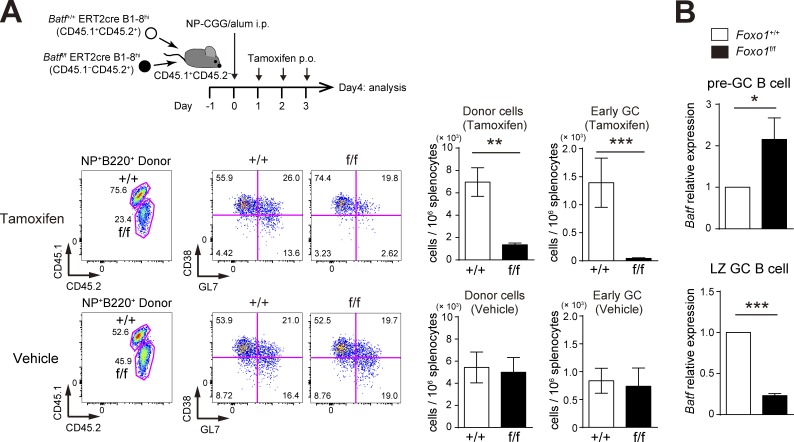
Figure 9.
BATF is required for preGC B cell expansion and is up-regulated in Foxo1-deficient preGC B cells. (A, top) Schematic illustration of the experimental protocol. Batf+/+ ERT2cre B1-8hi (CD45.1+CD45.2+) and Batff/f ERT2cre B1-8hi (CD45.1−CD45.2+) B cells were co-transferred into recipient mice (CD45.1+CD45.2−), which were immunized with NP-CGG/alum i.p. on day 0. Mice were administered tamoxifen or vehicle p.o. for 3 d and analyzed on day 4. (bottom left) Flow cytometry of NP-specific donor B cells (CD45.2+B220+NP+). (bottom right) Histograms showing the cell number of total donor cells (CD45.2+NP+B220+) and early GC B cells (CD45.2+NP+B220+GL7+CD38−) in 106 splenocytes. n = 4 biological replicates. (B) Real-time qPCR analysis of Batf mRNA expression in control and Foxo1-deficient B1-8hi preGC (donor B220+NP+CD38+GL7+) and LZ GC B cells (donor B220+NP+GL7+CD38−CD86hiCXCR4lo). preGC B cells and LZ GC B cells were prepared from mice as described in Fig. 1 C and Fig. 2 A, respectively. n = 3 biological replicates. Error bars represent SD. Data are representative of three (A) or two independent experiments (B). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; paired Student’s t test (A) and unpaired Student’s t test (B).