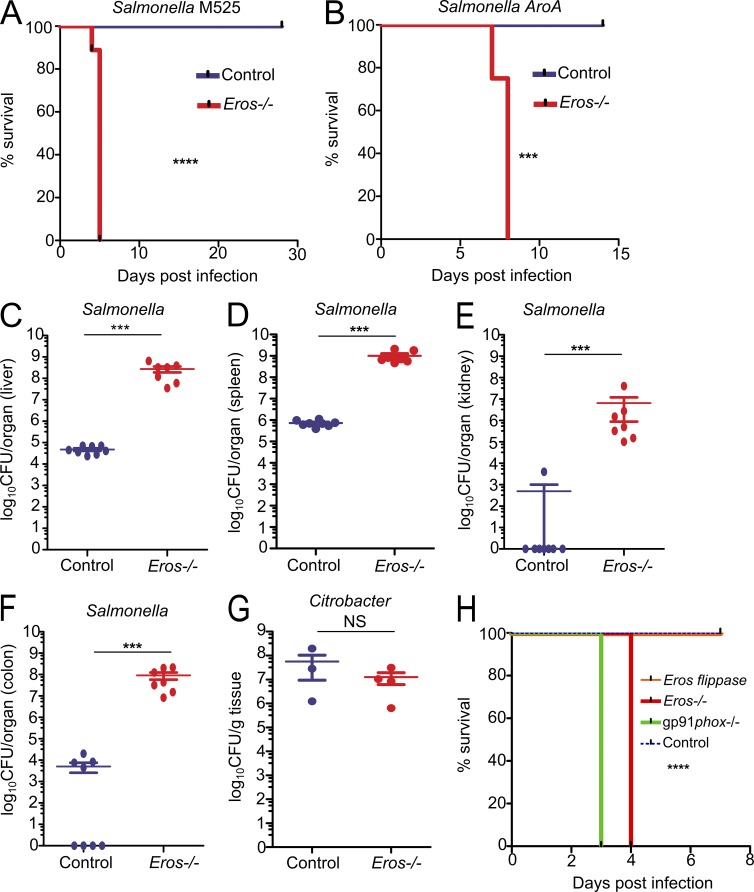
Figure 1.
Eros is essential for host defense against S. Typhimurium. (A and B) Survival of Eros−/− mice after i.v. challenge with S. Typhimurium M525 (A) or after oral challenge with S. Typhimurium ΔaroA (B). Data in A show eight mice per group and are representative of greater than five independent experiments. Data in B show eight mice per group and are representative of two independent experiments. (C–F) Bacterial burden expressed as CFU per organ in liver (C), spleen (D), kidney (E), and colon (F) at day 4 after infection with S. Typhimurium M525. Eight mice were used in each group. Results are representative of greater than five independent experiments (G) C. rodentium burden in colon after oral challenge. Eight mice were used per group and data are representative of two independent experiments. (H) Survival of control (eight mice), Eros-deficient (five mice), gp91phox-deficient (four mice), and Eros-sufficient flippase mice (repaired Eros allele; eight mice) after infection with 5 × 105 CFU of S. Typhimurium M525. Data are representative of two independent experiments. The P-value shown in H denotes the significant difference in survival between Eros-flippase and Eros-deficient mice. Error bars represent the SEM. ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Data in A, B, and H were analyzed by Log-Rank test and data in C–G were analyzed by Mann-Whitney test.