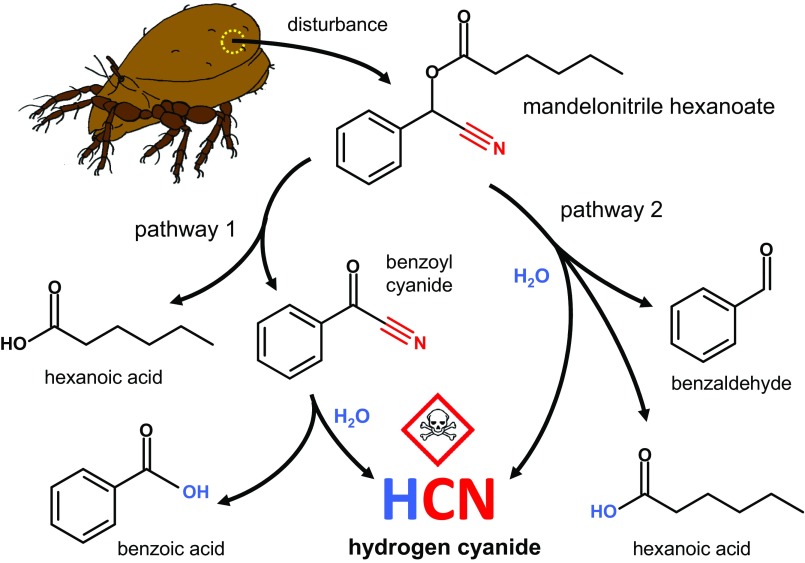
Fig. 2.
Expulsion and degradation of MNH from opisthonotal oil glands in the oribatid mite, Oribatula tibialis. Pathway 1: MNH is cleaved by a catalytic oxidation to benzoyl cyanide and hexanoic acid on the mite´s body surface. Subsequently, benzoyl cyanide hydrolyzes to benzoic acid and HCN. Pathway 2: Direct hydrolysis of the ester bond in MNH in the presence of moisture, resulting in the release of HCN, benzaldehyde, and hexanoic acid.