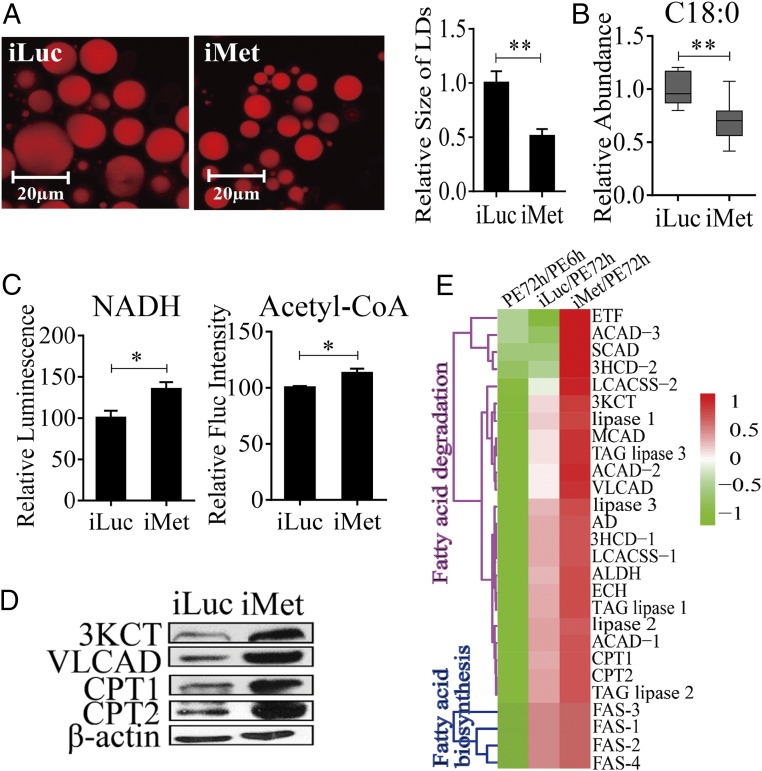
Fig. 3.
Effect of Met RNAi knockdown (iMet) on LM during the PE phase in A. aegypti female mosquitoes. (A) Nile red staining of iMet and iLuc controls in female mosquito FBs. The relative LD sizes were decreased significantly after iMet treatment. (B) GC-MS analysis showing reduced FFA levels (C18:0) in iMet mosquitoes. RNAi knockdown of Met treatments was normalized to iLuc. At least six independently collected samples were used for each treatment. (C) NADH and acetyl-CoA levels in iMet and iLuc mosquitoes. Measurements were normalized to the total protein in each treatment. iMet results were further normalized to iLuc. At least three independently collected samples with six mosquitoes were used for each treatment. (D) Western blot showing increased levels of catabolic LM enzymes in the FBs of iMet mosquitoes. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (E) Heat map representing transcripts of LM-related genes in iMet mosquitoes. Error bars in A–C represent the SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.