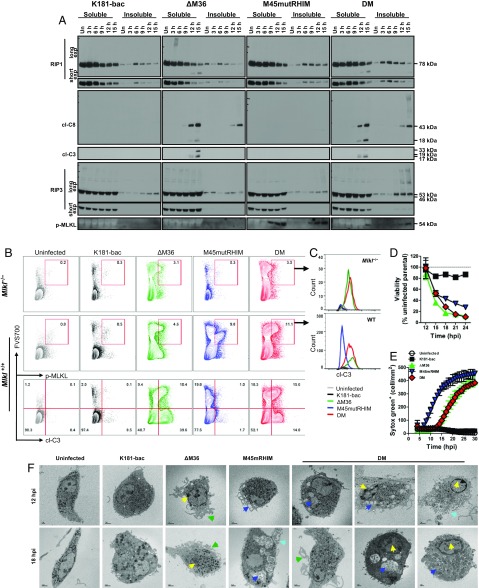
Fig. 2.
Double-mutant virus infection induces caspase-8–mediated apoptosis with delayed RIP3-dependent necroptosis. (A) Western blots showing RIP1, RIP3, cl-C8, cl-C3, and p-MLKL levels in BMDM. Cells were either uninfected or infected (MOI = 10) with K181-bac, ΔM36, M45mutRHIM, or double-mutant virus for the specified times. (B and C) Flow cytometry plots of virus-infected Mlkl−/− and Mlkl+/+ BMDMs at 15 hpi showing (B) FVS700 with p-MLKL or cl-C3 expression or (C) cl-C3 expression by FVS700+ p-MLKL+ cells. (D) Change in BMDM viability over time after infection. Horizontal dotted line indicates 100% viability. (E) SYTOX Green accumulation over time in permeable, necrotic BMDMs after infection. (F) Transmission electron microscopy images of BMDMs either uninfected or infected 12 and 18 hpi with specified virus (MOI = 10). Apoptosis markers: yellow arrows, condensed chromatin; green arrows, ruffling/blebbing. Necroptosis markers: dark blue arrows, vacuoles; light blue arrows, lysis.