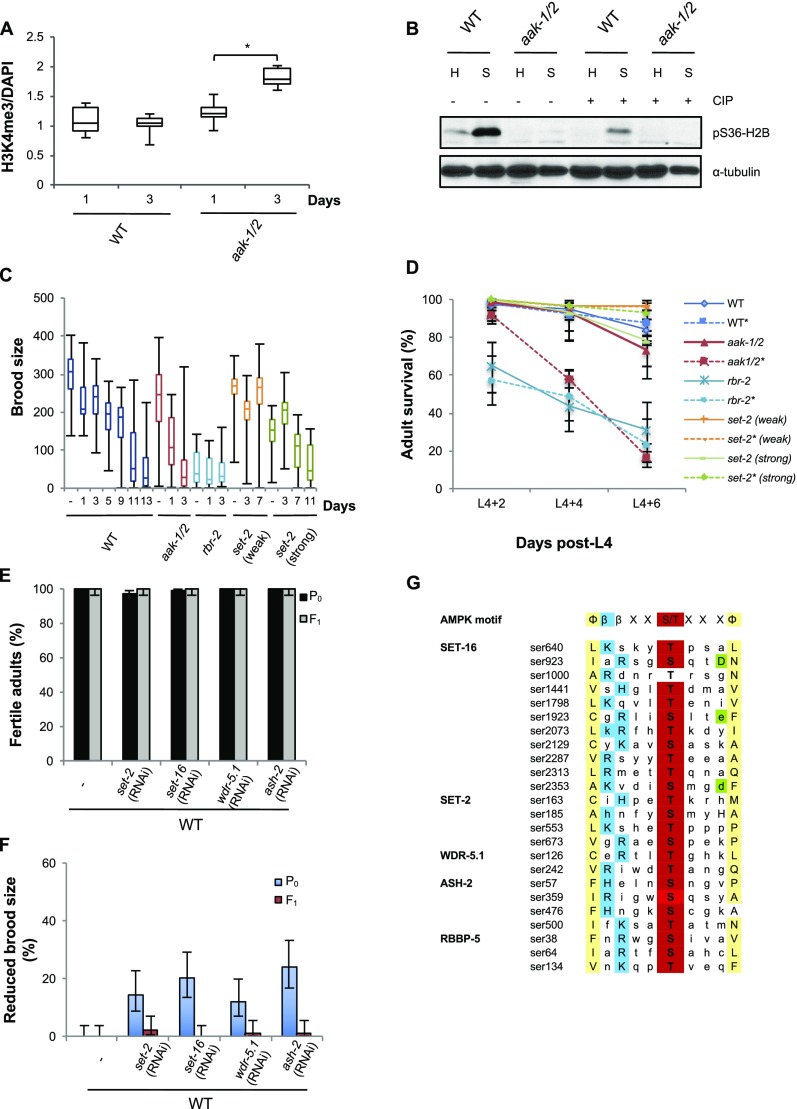
Fig. S3.
Post L1-diapause AMPK mutant animals accumulate H3K4me3 that is dependent on SET-2 histone methyltransferase. (A) Post-L1 diapause aak-1/2 L1 larvae have abnormally high levels of H3K4me3 in their PGCs. Wild-type and aak-1/2 L1 larvae were maintained either 1 or 3 d without food in the L1 diapause then immunostained with antibodies that recognize H3K4me3 and counterstained with DAPI. H3K4me3 levels were quantified and normalized to DNA content (DAPI) in the PGCs; n ≥ 15 different animals. *P < 0.05 (one-tailed t test). (B) H2B phosphorylation is induced by starvation and is AMPK-dependent. Western blot performed using antibodies against the H2 phosphorylated S36 epitope (ECM Biosciences) using whole-animal extracts from animals subjected to 3 d in the L1 diapause (“S” for starved) or nonstarved L1 extracts (“H” for healthy) treated with CIP phosphatase (+), or not (−), to show specificity for the phosphorylated isoform. (C and D) A misregulation of histone methyltransferase results in brood-size defects and premature lethality in post-L1 diapause AMPK mutants. L1 larvae of the following genotypes: set-2 (n4589) (a strong allele) or set-2 (ok952) (a weak allele), or the demethylase rbr-2 (tm1941), were subjected to varying periods in the L1 diapause then recovered on plates with food and grown to reproductive maturity. (C) The F1 brood size of resulting fertile adults was scored and represented in box plot format; n ≥ 40 per genotype per condition. (D) rbr-2 mutants phenocopy the premature adult death of post-L1 diapause aak-1/2 animals. Wild-type, aak-1/2, set-2, and rbr-2 L1 larvae were maintained in the L1 diapause for 3 d (*) or not starved (–), then recovered to replete plates and their post-L4 stage survival was scored every 2 d; n ≥100 animals per point. (E and F) Reducing the COMPASS activity by soaking animals in dsRNA that corresponds to each of the COMPASS components during the 3-d period in the diapause does not affect (E) the fertility of wild-type animals either in post-L1 diapause animals or, (F) the brood size of their subsequent F1 generation. Error bars: 95% CI; n ≥ 100 per condition from three independent experiments. (G) Two histone methyltransferases (SET-2 and SET-16) and associated components of the COMPASS complex are enriched for consensus AMPK phosphorylation sites. Peptide sequences were compared with the described AMPK consensus site described by Gwinn et al. (40) (AMPK motif) and aligned for comparison. There is a significant enrichment (Fisher exact test, P = 2.8 × 10−7) in proteins with at least one AMPK consensus phosphorylation recognition motif within the COMPASS complex. Red, phosphoacceptor site (Ser/Thr); yellow, hydrophobic residues; blue, basic residues; green, acidic residues. To perform Fisher’s exact test: 11,353 proteins were identified that have a single AMPK consensus site among a total of 20,405 Caenorhabditis elegans proteins (excluding isoforms) according to Wormbase release WS246. This enrichment is still valid even when protein size is taken into consideration: 24 of 11,353 AMPK consensus sites are found in COMPASS complex components (2.1%). This is significantly different from the number expected according to random distribution. All of the COMPASS components together contain 11,130 aa for a total of 8,378,701 aa (1.3%); exact binomial test P = 0.00211.