Figure 1. Crystal structure of yeast IPMK reveals positions of amino acids involved in IPMK substrate specificity and PPIs.
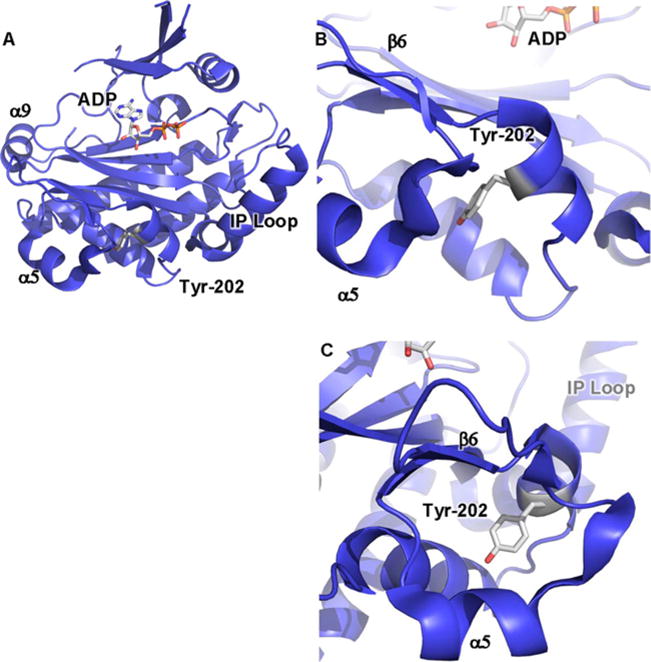
(A) Ribbon cartoon of the 2.0 Å crystal structure of S. cerevisiae IPMK [43] (PDB: 2IF8), one of only two IPMK structures solved to date, the other being the A. thaliana plant IPMK [30] (result not shown, PDB: 4FRF). The helix in the lower right labelled as ‘IP loop’ is the inositol binding helix, instilling much of the substrate specificity to the enzyme. ADP indicated as sticks. α9, α5 and β6 elements have been suggested to be a PPI surface. (B) Tyr174 of the mouse IPMK is phosphorylated in response to glucose and mediates IPMK interaction with AMPK, through an unknown mechanism. Tyr174 is conserved in human IPMK (Tyr191) and the depicted yeast IPMK (Tyr202), as indicated. (C) As in (B), rotated 90°.
