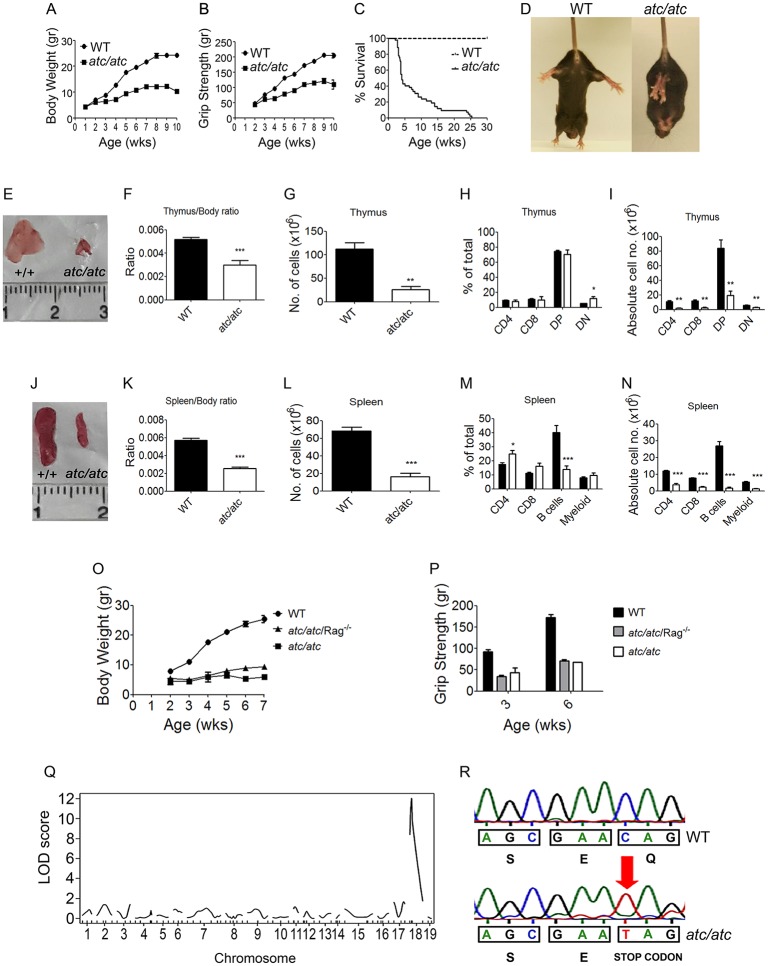
Fig 1. Clinical characterization of the ataxic phenotype and identification of the causal mutation in Slc25a46.
(A) Reduced body weight gain (n = 20 per group), (B) muscle weakness (n = 20 per group), (C) premature lethality (n = 40 per group) and (D) loss of hind limb extension reflex during tail suspension in ataxic (atc/atc) mice as compared to sex matched control (+/+ or atc/+) littermates. (E) Representative thymi dissected from WT and atc/atc mice. (F) Reduced thymus/body weight ratios in atc/atc mice as compared to WT littermates (n = 17 per group) accompanied by (G) lower total thymocyte numbers in atc/atc mice (n = 4–5 per group). (H) Percentages and (I) absolute numbers of thymic subpopulations (CD4+, CD8+, DP: Double Positive CD4+CD8+, DN: Double Negative CD4-CD8-) in WT (black columns, n = 5) and atc/atc (white columns, n = 4) littermates as determined by flow cytometry after staining with antibodies against CD4 and CD8. (J) Representative spleens dissected from WT and atc/atc mice. Reduction in spleen/body weight ratios in (K) atc/atc mice as compared to WT littermates (n = 17 per group) and (L) total splenocyte numbers (n = 5 per group). (M) Percentages and (N) absolute numbers of splenic subpopulations in WT and atc/atc littermates (n = 5 per group) through flow cytometry after staining with antibodies against CD4, CD8, B220 (B cells), CD11b and Gr1 (Myeloid). Atc/atc mice were crossed with Rag2 deficient mice (Rag-/-) that lack mature T and B lymphocytes and (O) body weight curves as well as (P) grip strength measurements demonstrate that the neurological phenotype is not reversed (WT and atc/atc/Rag-/-, n = 5 per group; atc/atc, n = 3). Data represent mean values ± SEM. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test was performed for statistical analysis. * p≤0.05; ** p≤0.01; *** p≤0.001. (Q) Through genome-wide linkage analysis the causal mutation was mapped on chromosome 18. (R) Sequencing of genomic DNA samples from WT controls (+/+) and atc/atc littermates revealed an exonic C-to-T transition (red arrow) in the Slc25a46 gene that introduce a premature stop codon.