FIGURE 2.
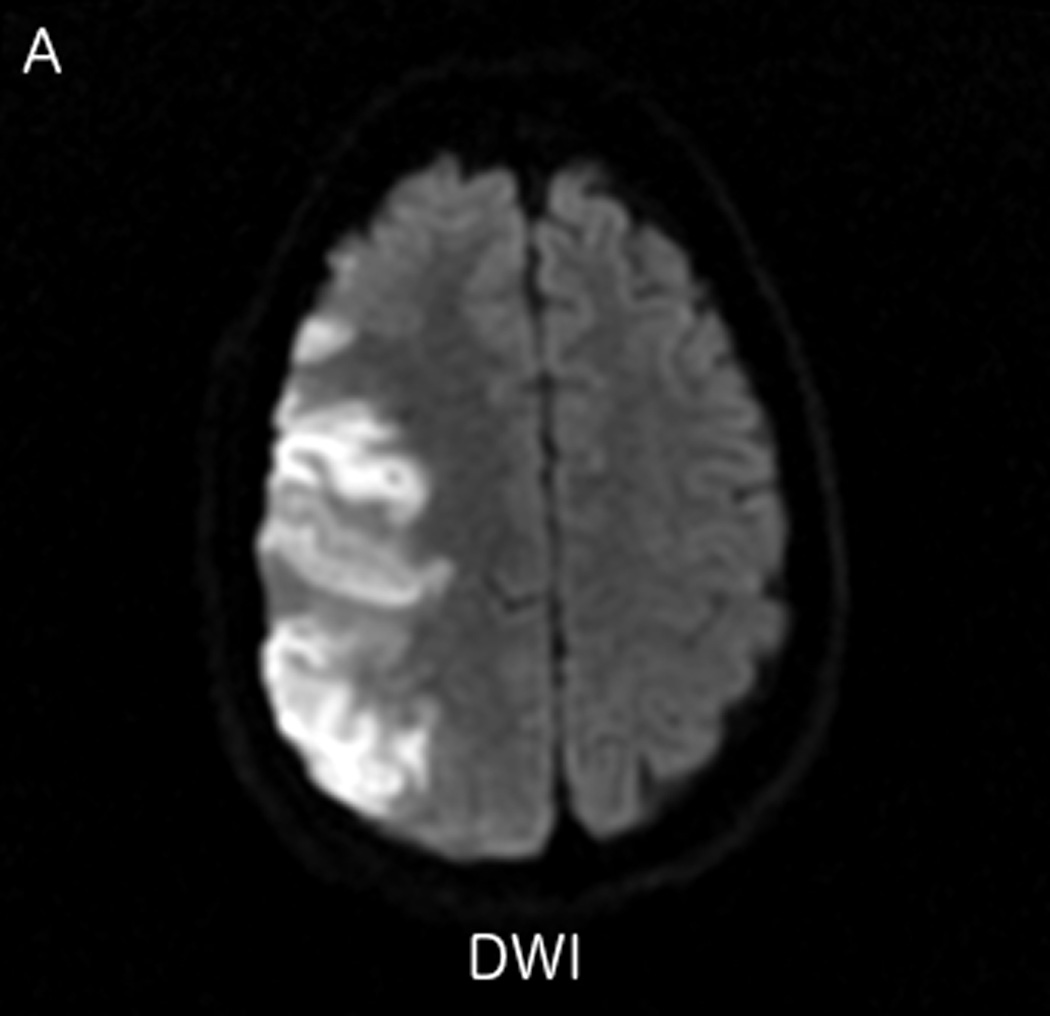
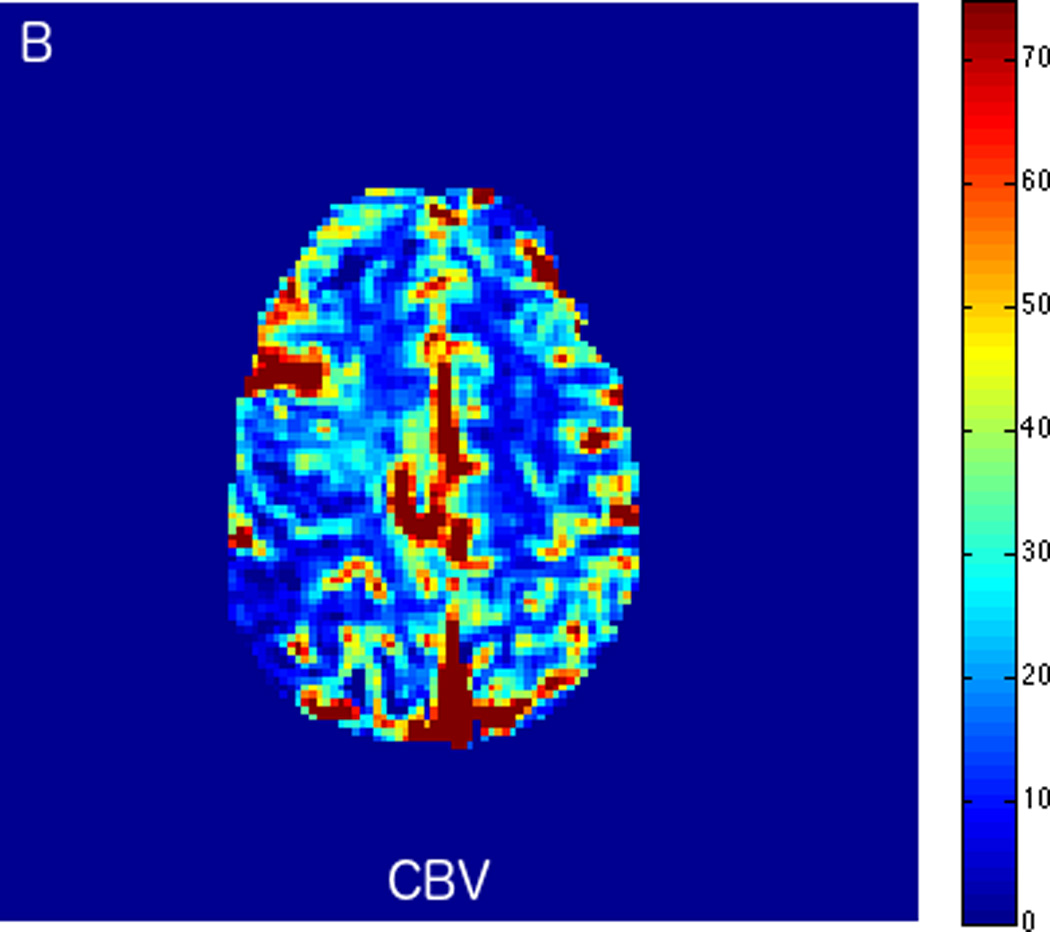
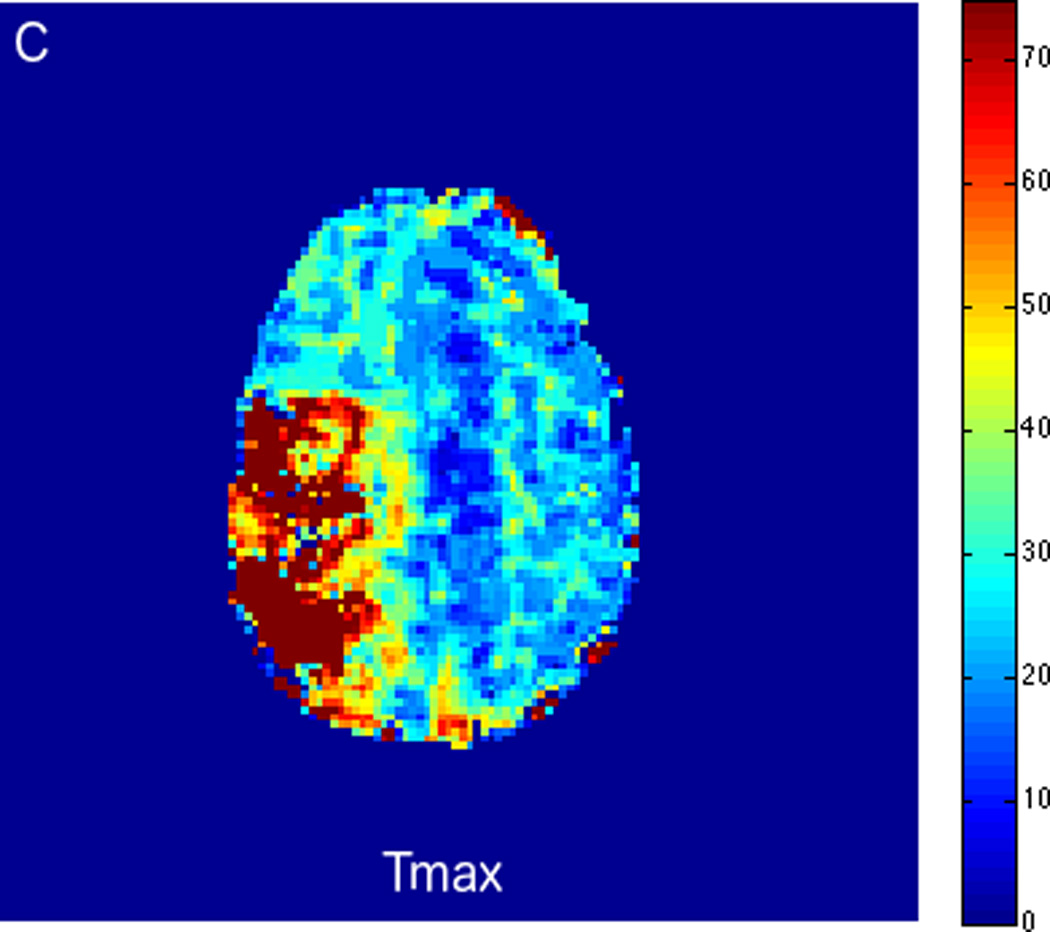
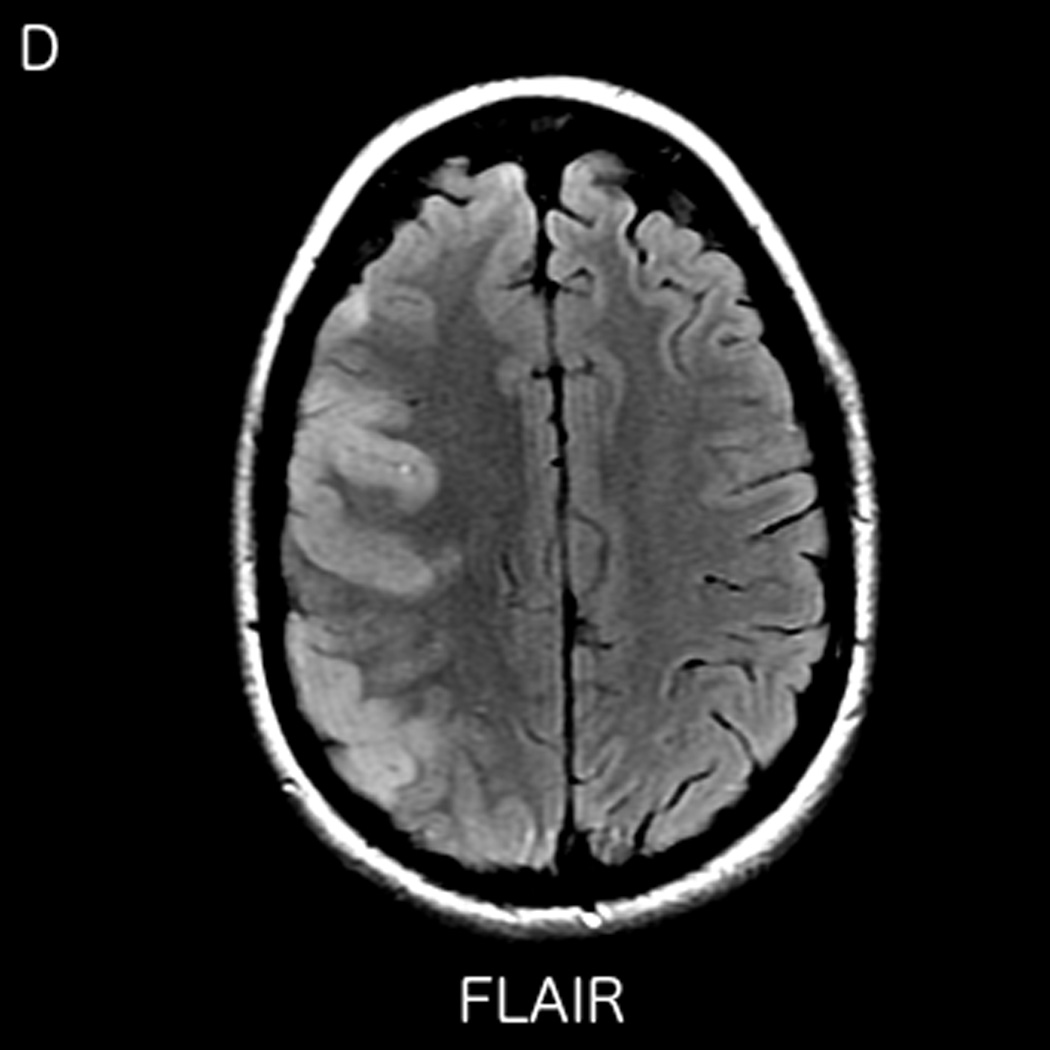
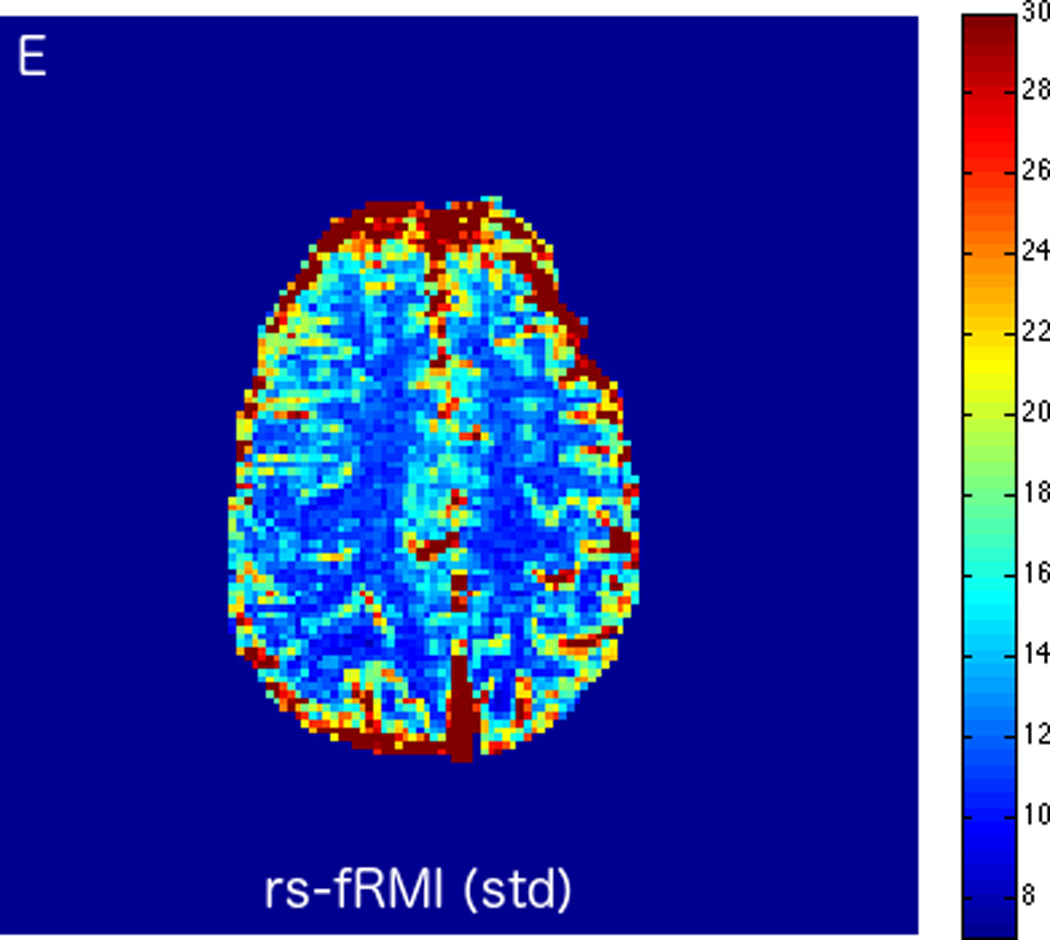
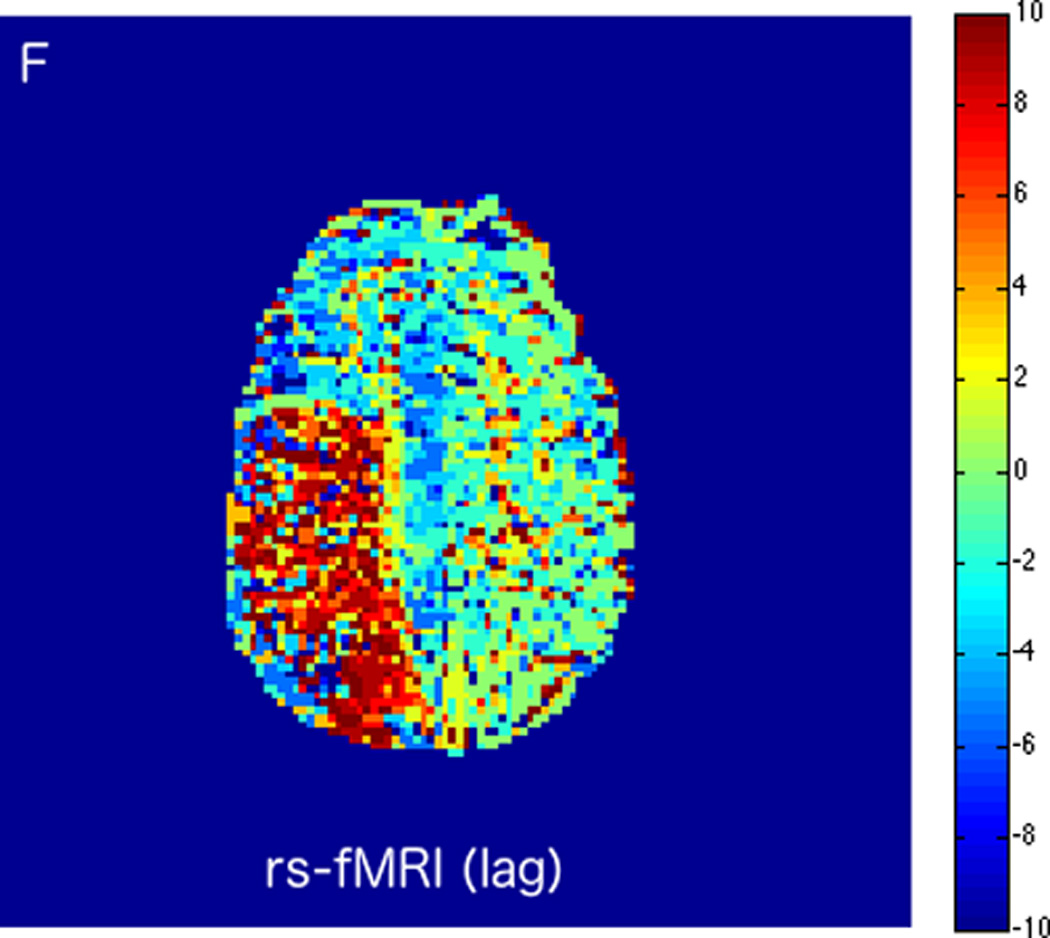
MRI including diffusion, perfusion with dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC), and resting-state BOLD fMRI in a 37-year-old female patient who presented with acute right-sided headache as well as left-sided facial droop and weakness (NIH stroke scale 15). DWI (A) and FLAIR (D) MR images show abnormal signal in the right middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory, compatible with a late acute to early subacute infarction. DSC perfusion images demonstrate mildly decreased cerebral blood volume (CBV) (B) and prolonged Tmax (C) in the right MCA territory. The standard deviation of low frequency fluctuations (E) and delay correlation analysis (F) from resting-state fMRI show excellent correlation with the respective DSC bolus perfusion maps. The perfusion defect is matched with the diffusion abnormality and represents completed infarction without penumbra.
