FIGURE 3.

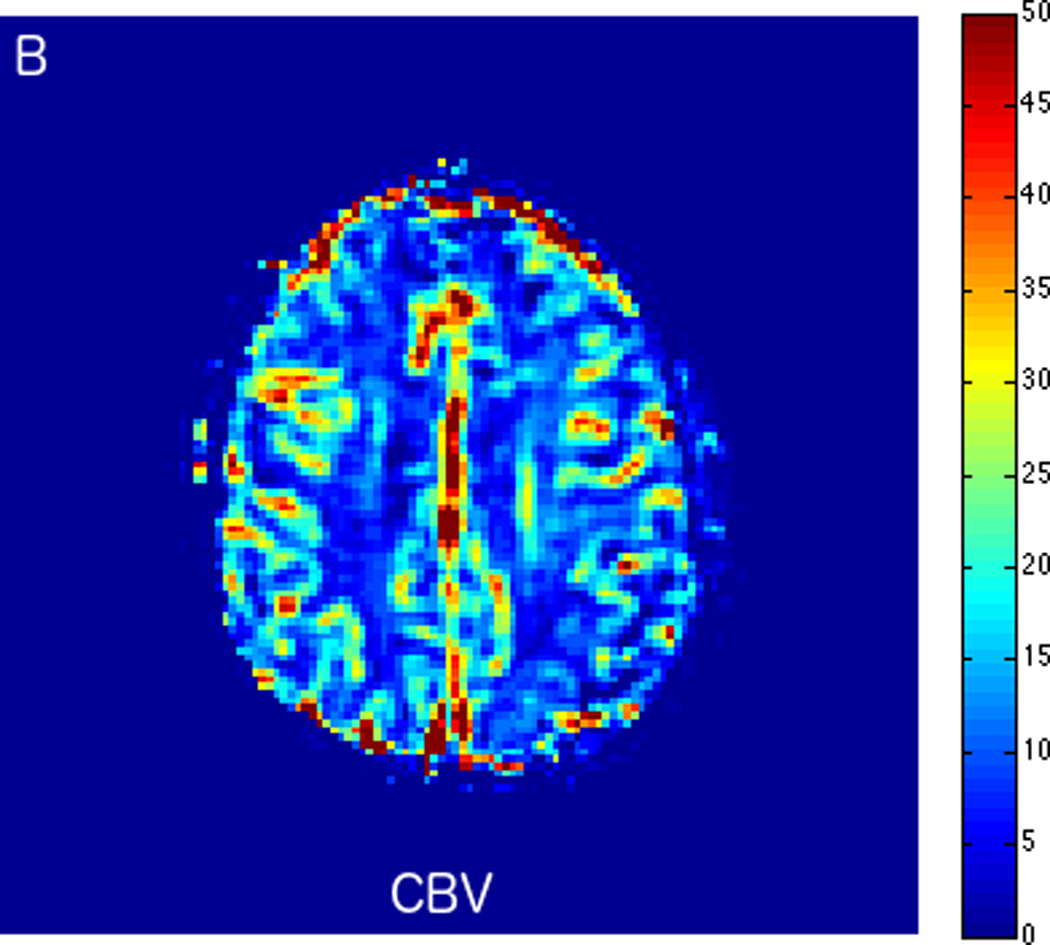
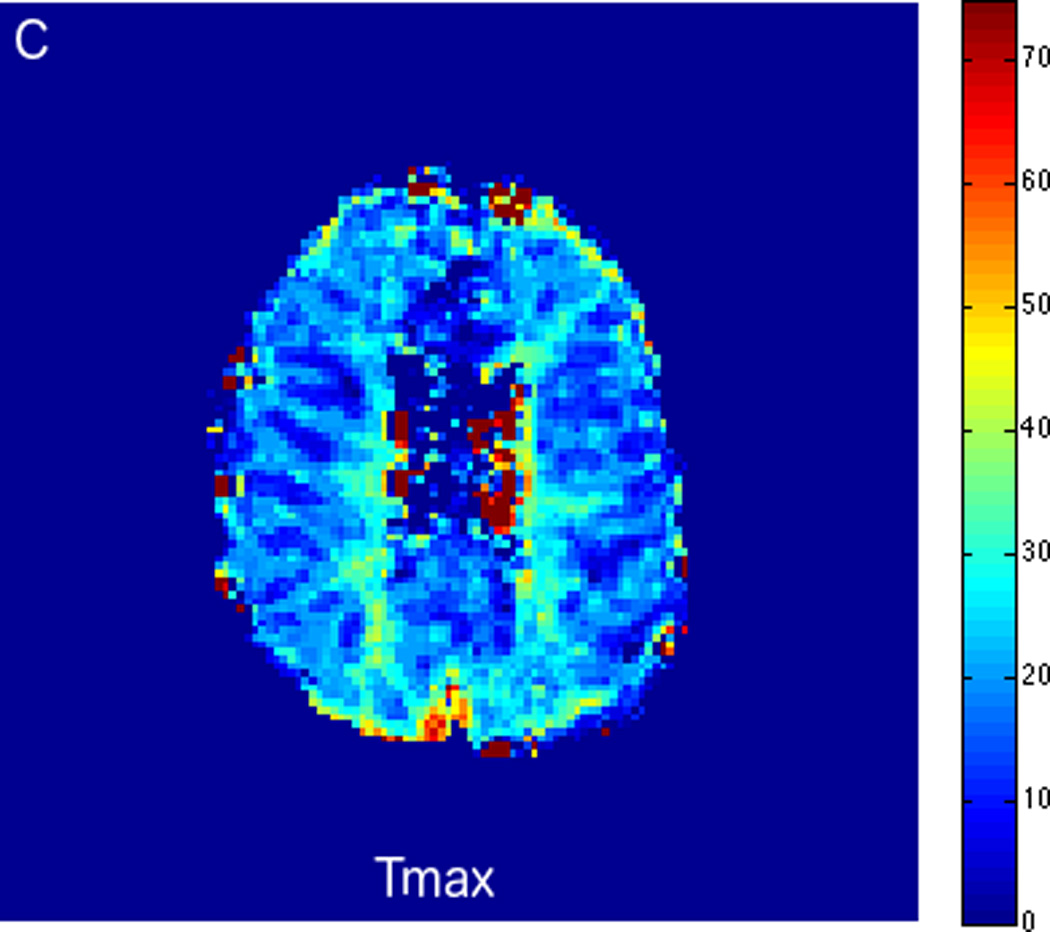
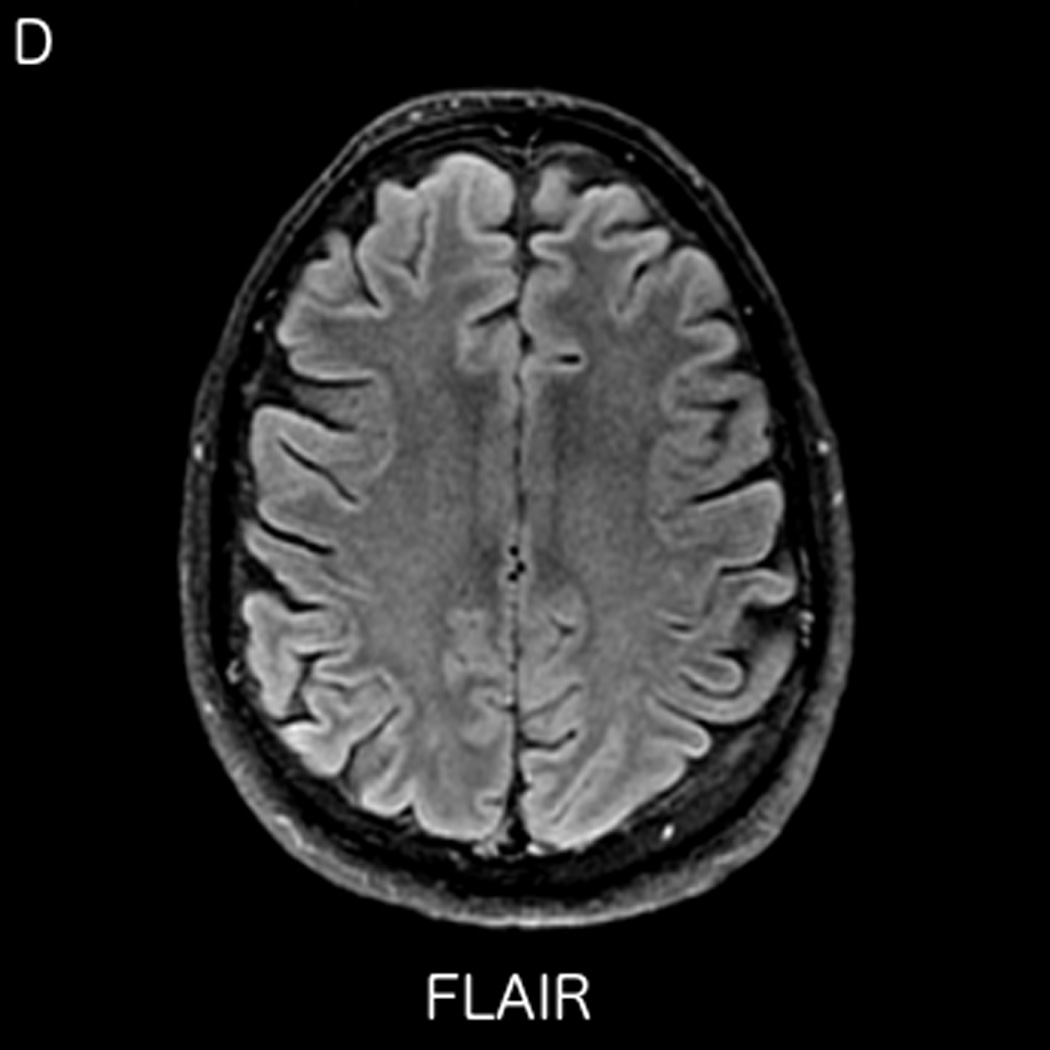
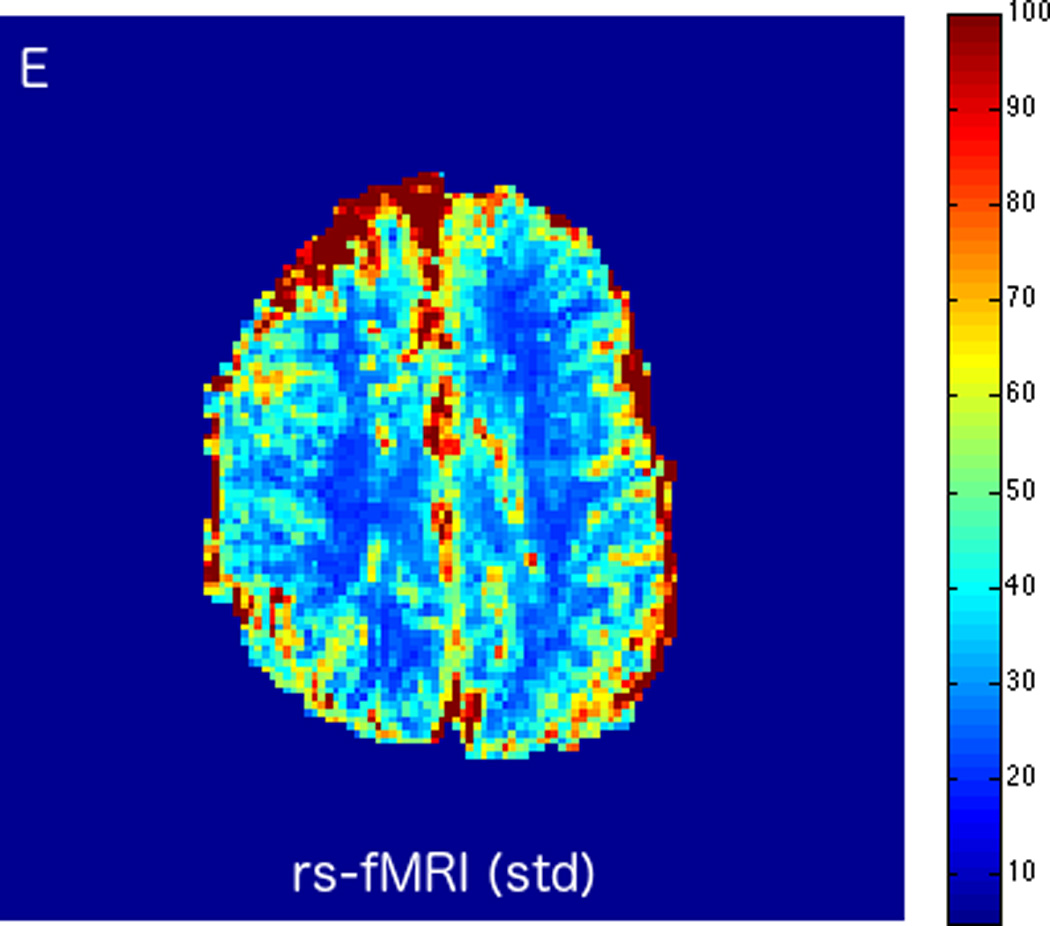
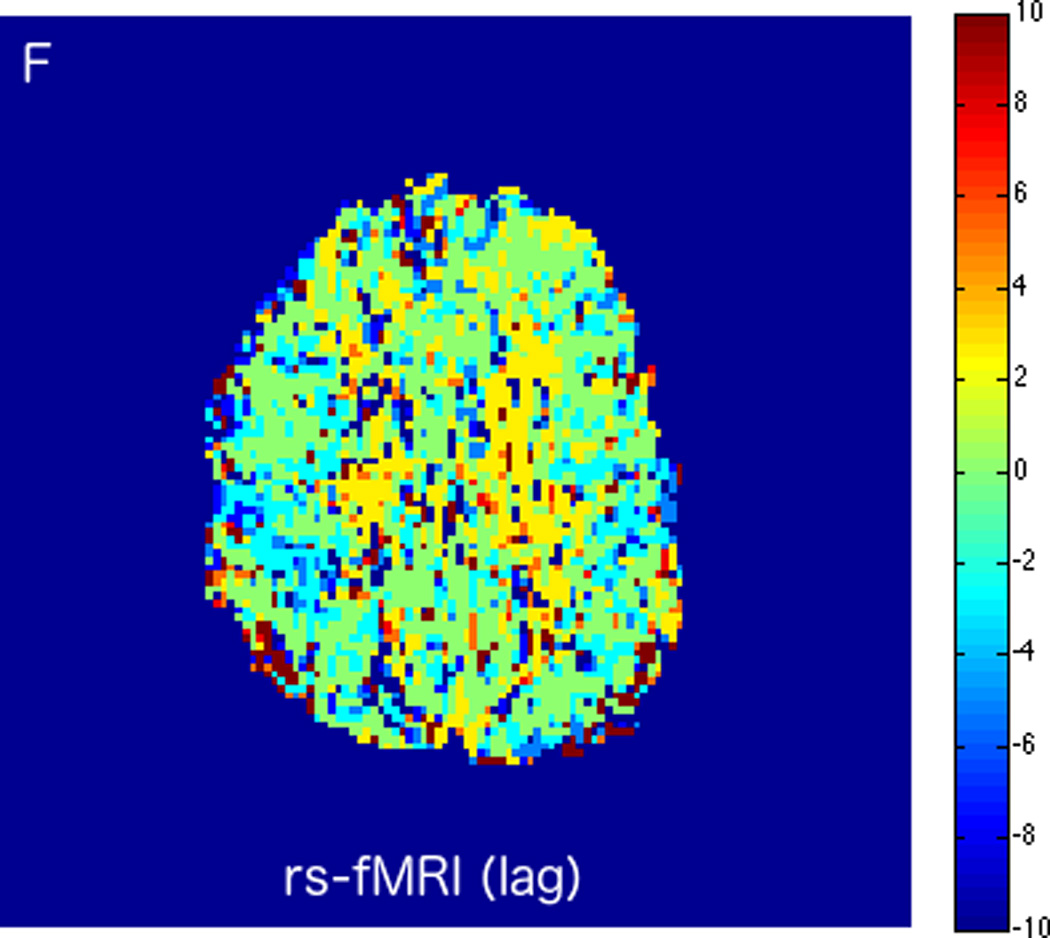
MRI including diffusion, perfusion with dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC), and resting-state BOLD fMRI in a 66-year-old male patient with history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes, who presented with acute left hand tingling, left mouth numbness, and left visual field cut (NIH stroke scale 3). CT angiography, which was performed prior to the MRI, showed occlusion of the right posterior cerebral artery (not shown), after which intravenous tPA was administered. DWI (A) and FLAIR (D) MR images demonstrate no cortical signal abnormality to suggest the presence of acute infarction. DSC perfusion images demonstrate normal and symmetric cerebral blood volume (CBV) (B) and Tmax (C). The standard deviation of low frequency fluctuations (E) and delay correlation analysis (F) from resting-state fMRI demonstrate excellent correlation with the corresponding DSC perfusion maps. These findings indicate complete recanalization of the occluded vessel without evidence of ischemia. Follow-up MR angiography confirmed resolution of the previously identified right posterior cerebral artery occlusion (not shown).
