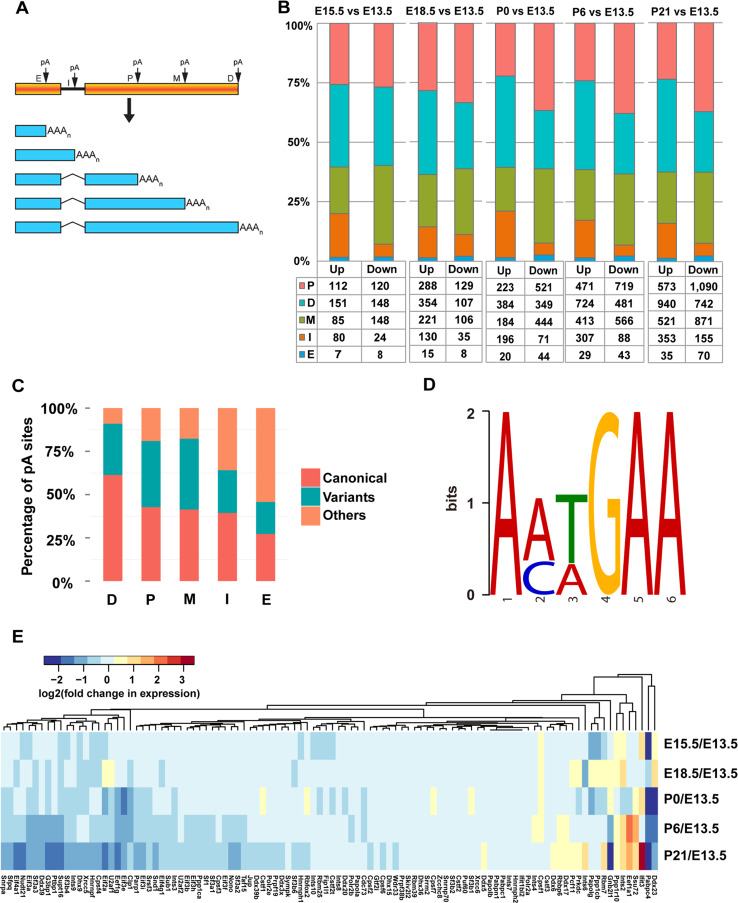
Fig. 5.
Preferential usage of weak proximal pA sites at the early developmental stages. a Schematic representation of different types of pA sites. E, I, P, M, and D indicate exonic, intronic, proximal, middle, and distal pA sites, respectively. b Number of downregulated (Down) and upregulated (Up) pA sites of different types when later stages are compared to E13.5. c Frequency of the PAS for different types of pA sites. d Hexamer sequence motif identified by MEME analysis of the upstream 10–30 nt region of the pA sites without canonical PAS or the 12 most common variants in human. The log-likelihood ratio (1421) and E value (2.9E−012) are significant compared with the zero-order Makov model using the background letter frequencies. e Heat map of fold change in expression level (RPM in logarithm scale) of 94 cleavage and polyadenylation-associated (CPA) factor genes when later stages are compared to E13.5. The expression level is approximated by the summed tags of the pA sites assigned to the same gene