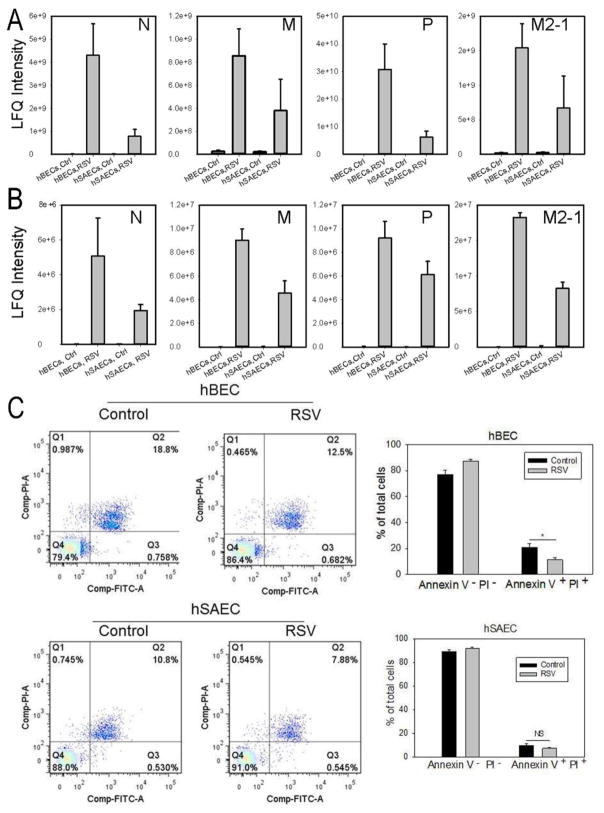
FIGURE 1. RSV replication and its effects on tert-immortalized epithelial cells.
(A). Tert-hBECs or tert-hSAECs were infected with sucrose cushion-purified pRSV (MOI=1.0). 24 h later, cells were lysed and a panel of RSV nucleoprotein (N), matrix protein (M), phosphoprotein (P) and matrix M2-1 (M2-1) was quantified by LC-MS/MS. RSV proteins were not detected in mock-infected cells, and dramatically increased with infection. Note that RSV replicates more effectively in tert-hBECs. (B). CM was analyzed for RSV proteins as in Fig. 1A. (C). Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) showing percentage of apoptotic (lower right quadrant –annexin V-positive, PI-negative) and necrotic (upper right quadrant – annexin V-, PI-positive) cells after 24h of RSV infection. Bottom left, histogram of percentage of apoptotic tert-hBECs infected with RSV. Bottom right, histogram of percentage of apoptotic tert-hSAECs after RSV infection. Results are means ± SD of duplicates measured twice.