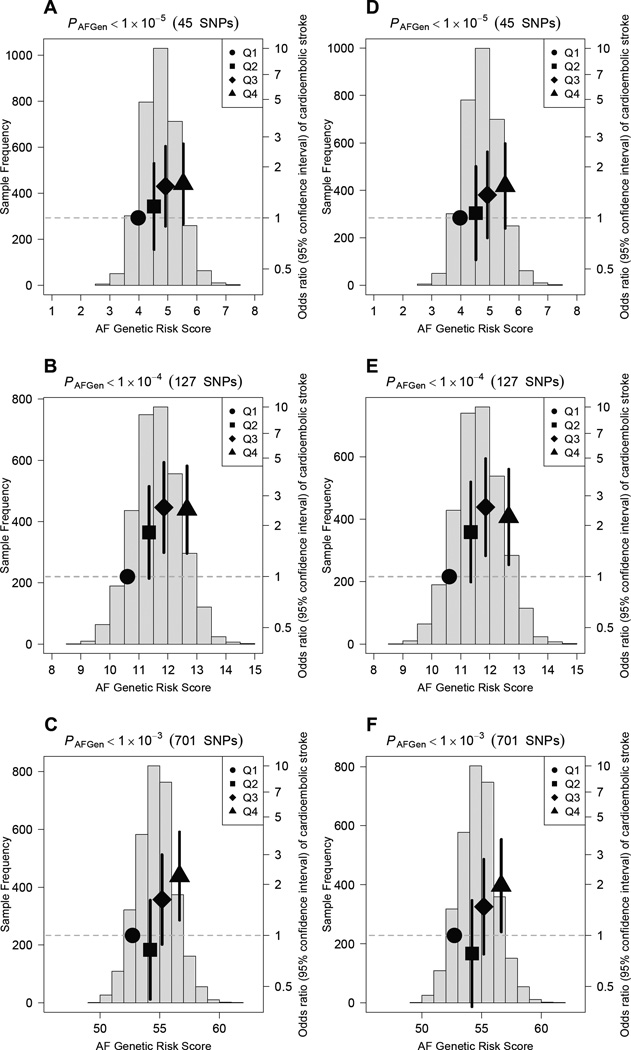
Figure 2.
Risk of cardioembolic stroke in MGH-GASROS according to atrial fibrillation genetic risk.
Odds ratios for cardioembolic stroke in relation to atrial fibrillation genetic risk scores among cardioembolic stroke cases and 3,028 controls. Blue histograms show distributions of genetic risk scores among cases and controls. Black dots indicate odds ratios for stroke for each quartile of genetic risk scores (bars indicate 95% confidence intervals). For panels A–C, genetic risk scores were based on 45 (A), 127 (B), and 701 (C) SNPs among 202 cardioembolic stroke cases (including 70 with known AF) and controls. For panels D-F, genetic risk scores were based 45 (D), 127 (E), and 701 (F) SNPs among 152 cardioembolic stroke cases (none with known AF) and controls. SNP totals may not equal those used in the incident atrial fibrillation analysis since some SNPs were unavailable in MGH-GASROS, in which case proxies were used when available (Supplemental Table 1).