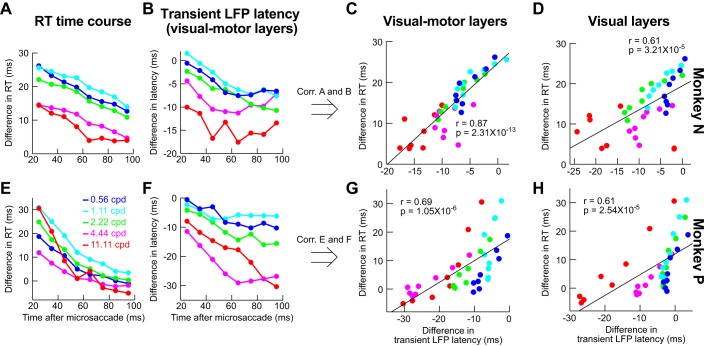
Fig. 11.
Correlation between LFP modulation parameters and behavioral effects of suppression. This figure is formatted similarly to Fig. 6, except that we have plotted LFP time courses instead of firing rate time courses. Specifically, in B and F, we plotted the time course of LFP stimulus-evoked response latency (e.g., Fig. 9B) as a function of spatial frequency and time after microsaccades. The correlation between this latency in visual motor layers and behavior was better (C and G) than in visual layers (D and H). Thus it is again the visual motor layers that are better predictors of behavior, as in Fig. 6, although firing rates (Fig. 6) showed higher correlations to behavior in general. Note that we also measured correlations between behavior and LFP stimulus-evoked response strength rather latency (data not shown), but the LFP response latency always showed the better correlations with behavior.