Figure 1.
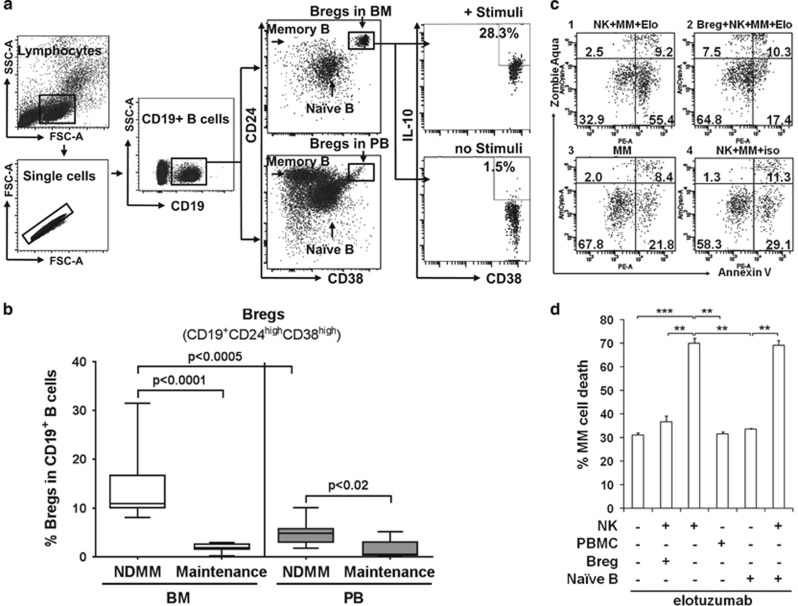
Regulatory CD19+CD24highCD38high B cells with immunosuppressive properties are defined within BM more distinctly than PB in MM. (a) Bregs are phenotypically identified by flow cytometry as a distinct subset of CD19+CD24highCD38high cells within BM, but not PB, from the same MM patient. Shown is a representative analysis of paired patient BM and PB with two separate B-cell populations: CD19+CD38intCD24int B cells (primarily naive B cells) and CD19+ CD24− CD38low/− B cells (primarily memory B cells). BM-derived Bregs producing IL10 are significantly increased from 1.5 to 28.3% after stimulation with PMA and LPS (+ stimuli). (b) The percentages of BM-derived Bregs within CD19+ B cells are significantly higher in the NDMM group compared to the group who responded to treatment (maintenance) (n=10 for each group). (c and d) Bregs inhibit NK cell-mediated ADCC against MM target cells by elotuzumab. (c) Results of inhibition of BM-derived Bregs from a representative MM patient sample. 1, NK cells+MM cells+elotuzumab (elo); 2, BM-derived Bregs+NK cells+MM cells+elo; 3, MM cells alone; 4, NK cells+MM cells+isotype IgG1 control. (d) Shown are summary of % patient MM cell lysis in the presence or absence of BM-derived Bregs or naive B cells from NDMM (n=3), with or without effector cells. Data represent mean±s.d. for each group; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, Student's t-test. FCM, flow cytometry; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PMA, phorbol myristate acetate.