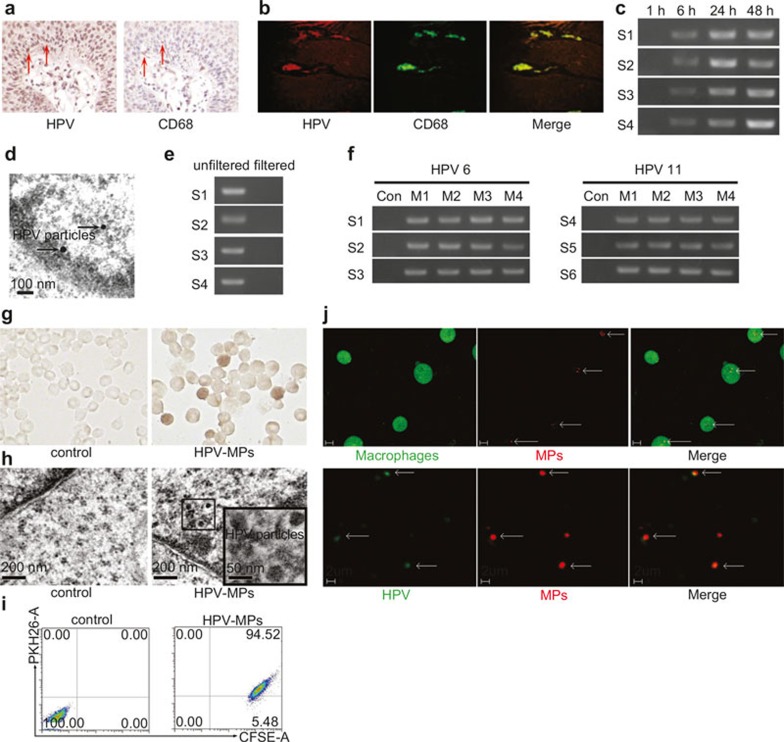
Figure 1.
Macrophages can be infected by HPV. (a and b) Analysis of macrophages in genital warts by immunohistochemical staining (a) and immunofluorescent methods (b). (c) Macrophages derived from PBMCs were incubated with genital wart supernatants for 6 hours. The incubation media were washed away and macrophages were cultured in fresh RPMI 1640 culture medium for different times. The expression of HPV E6 mRNA in macrophages was detected by RT-PCR. S1–S4 represented four samples, respectively. (d) Virus particles in 24-hour re-cultured macrophages were observed under an electron microscope. (e) Genital wart supernatants were filtered with 100 nm size filters and used for incubation with macrophages for 6 hours. The incubation media were washed away and macrophages were cultured in fresh RPMI 1640 culture medium for 24 hours. The expression of HPV E6 mRNA in macrophages was detected by RT-PCR. S1–S4 represented four samples, respectively. (f) MPs were isolated from genital wart supernatants and incubated with macrophages for 6 hours. The incubation media were washed away and macrophages were cultured in fresh RPMI 1640 culture medium for 24 hours. The expression of HPV E6 mRNA in macrophages was detected by RT-PCR. S1–S6 represented four samples, respectively. MPs isolated from healthy donor peripheral blood were used as control. M1–M4 represented microparticles generated from four generations of macrophages, respectively. (g and h) HPVs were observed in macrophages in experimental group by immunocytochemistry (g) and electron microscopy (h). MPs isolated from healthy donor peripheral blood were used as negative control group. (i) The uptake of MPs by macrophages were analyzed by flow cytometry. (j) Two-photon microscopic analysis. Upper row: macrophages took up MPs. Lower row: HPV was included in MPs.