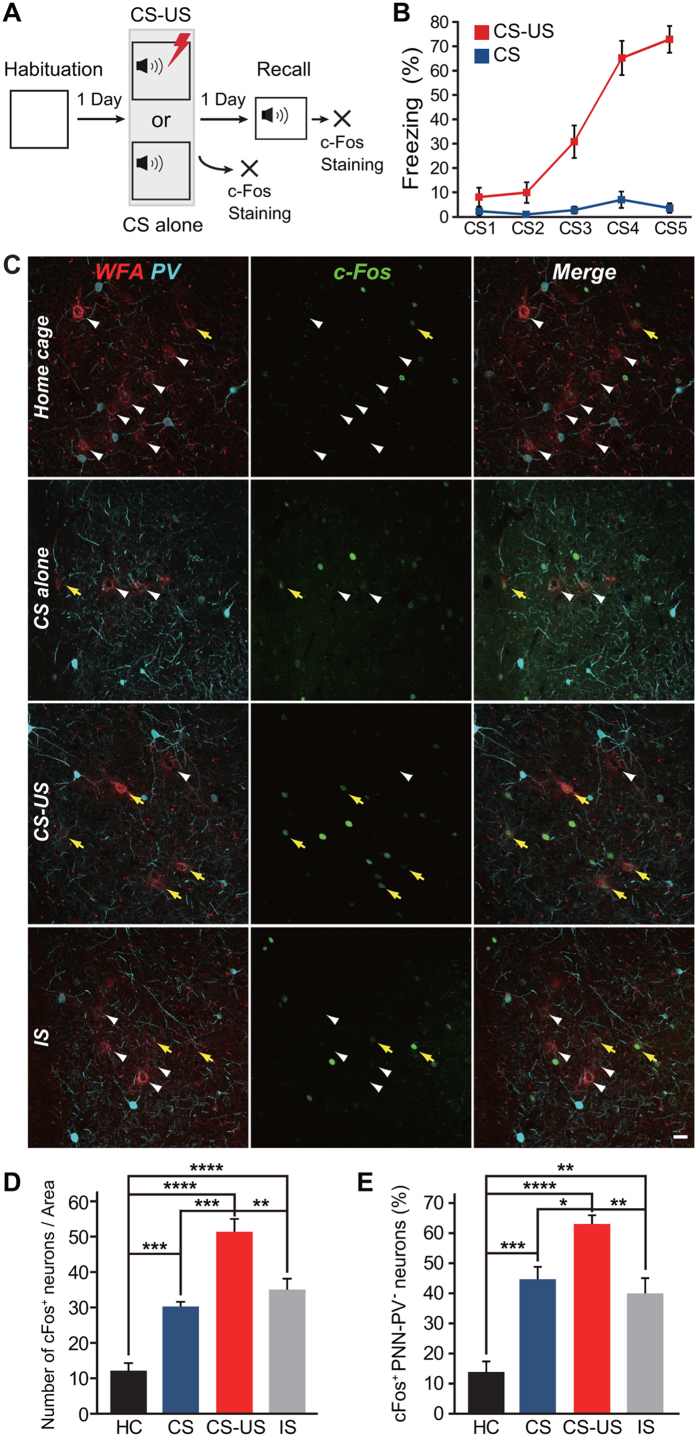
Figure 3. c-Fos expression in PNN-PV− neurons is induced by fear learning.
(A) The experimental schedule. (B) Tone-induced freezing in mice that received either tone only (blue line, n = 16) or tone-shock pairing (red line, n = 17). Error bars indicate the SEM. (C) Representative images showing WFA-labeling (red) and expression of PV (cyan) and c-Fos (green) in mice exposed to their home cage (HC; upper), CS-alone (middle upper), CS-US pairing (middle lower), or IS (lower). Yellow arrows indicate PNN-PV− neurons expressing c-Fos. White arrowheads indicate PNN-PV− neurons that do not express c-Fos. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Total number of neurons expressing c-Fos in mice subjected to HC (black, n = 6), CS-alone (blue, n = 6), paired CS-US (red, n = 5), and IS (gray, n = 6). Fear conditioning by CS-US pairing (****P < 0.0001 vs. HC), CS-alone training (***P < 0.001 vs. HC), and IS (****P < 0.0001 vs. HC) increases the number of neurons expressing c-Fos. (E) The probability of c-Fos expression in PNN-PV− neurons in mice subjected to HC, CS-alone, paired CS-US, and IS. Compared with animals in their HC and those exposed to CS-alone and IS, c-Fos is localized to PNN-PV− neurons in mice subjected to fear conditioning. Colors as in (D). Error bars indicate the SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.