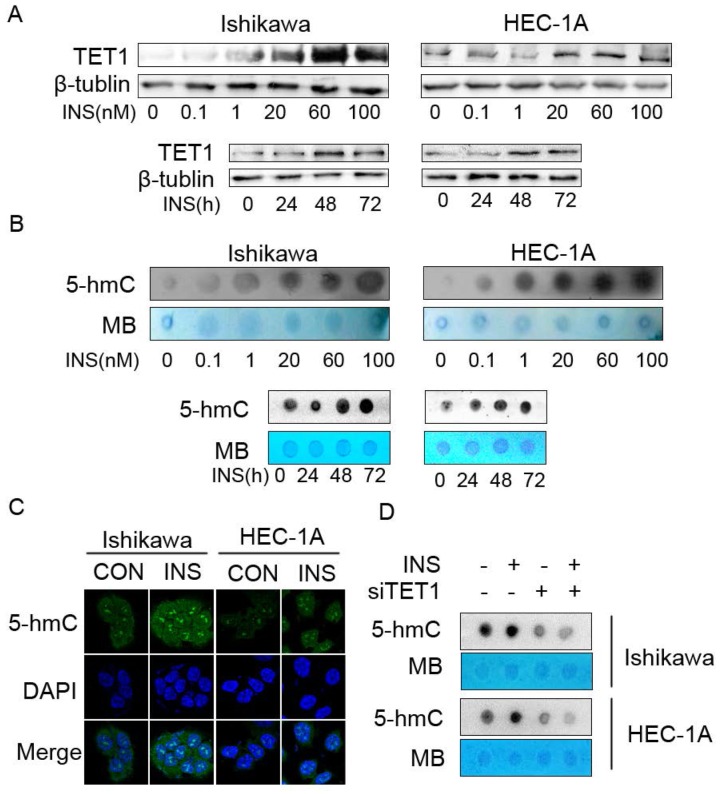
Figure 3.
Insulin microenvironment shows increased TET1 expression and genomic DNA hydroxymethylation. A. Insulin promotes TET1 expression in endometrial cancer cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Cells were treated by insulin at indicated dose for 48h (up panel) or by 100nM insulin for indicated period (bottom panel). TET1 expression was analyzed by western blot. B. Insulin promotes genomic DNA hydroxymethylation. Endometrial cancer cells were treated with insulin at indicated dose for 48 h (up panel) or 100nM insulin for indicated period (bottom panel). 5-hmC levels were detected by dot-blot in total DNA. C. Insulin induces 5-hmC expression in cell nuclear. Confocal staining showed increasing 5-hmC expression (green) in the nuclei of endometrial cancer cells after insulin (100nM) treatment for 48h. DAPI (blue) was used as a DNA dye to indicate cell nuclei. D. TET1 specific siRNA abolished insulin-induced 5-hmC level of global DNA. Dot blot was used to analyze 5-hmC status. * p < 0.05, **p < 0.01,***p < 0.001 compared to control.